Decades-spanning efforts to design systems capable of emulating human intelligence have enabled the rise of AI in business.
With AI adoption now snowballing across industries, the race is on to leverage AI tech and become first movers in their respective fields.
It’s clear that the future of modern industry will be increasingly defined by AI, and has become integral across all operations in nearly all sectors.
This article explores the many AI examples in industry today, from carbon capture and renewable sourcing in energy to fraud detection and cyber defense in finance and IT operations.
- 1. AI in finance
- 2. AI in energy
- 3. AI in manufacturing
- 4. AI in healthcare
- 5. AI in education
- 6. AI in retail
- 7. AI in eCommerce
- 8. AI in logistics and supply chain
- 9. AI in insurance
- 10. AI in HR
- 11. AI in cybersecurity
- 12. AI in marketing and sales
- 13. AI in IT operations
- Understanding AI risks across industries
- People Also Ask
1. AI in finance
The first example on our list, AI in finance, is finding its way into nearly all aspects of services and operations.
Deep-rooted processes at some of the industry’s leading financial institutions are being upended by artificial intelligence (AI).
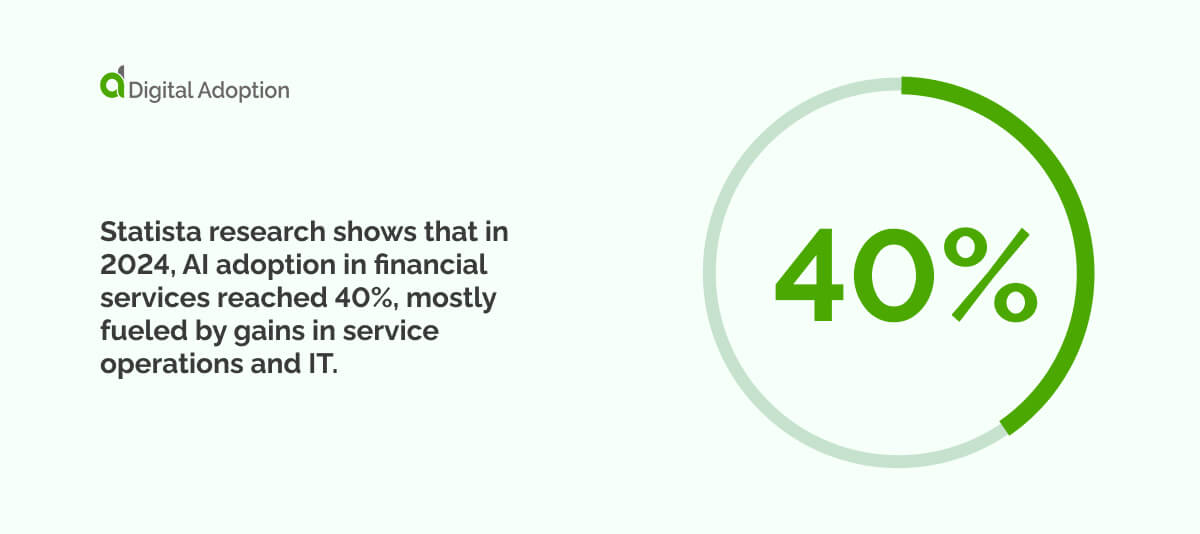
AI can now deliver uninterrupted monitoring for fraud detection, scanning customer accounts and transactions for unusual patterns. AI takes cybersecurity one step further, even being able to assess biometric behavior, such as the way users grip their device, typing rhythms, and unrecognized fingerprints, to flag actions that do not match known patterns.
AI is enabling next-gen financial technology (FinTech) through digital banking apps. Apart from instant money management, banking apps today offer intuitive AI agents that can answer questions using natural language processing (NLP) and predictive analytics for forecasting future savings.
AI-driven robo-advisories can even guide personalized portfolio and investment management. This is just the tip of the iceberg of how AI is spearheading innovation across the financial industry.
2. AI in energy
Much like finance, examples of AI in energy are plentiful. This industry underpins critical societal functions, from agriculture, government IT, and global-spanning logistics and supply chains.
AI advances in energy work to strengthen sector capabilities, from automated Smart grids that monitor conditions across the entire network. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) algorithms help AI build a single source of truth using data on real-time situations and infrastructure conditions.
The IoT connects physical sensors placed across substations and network nodes, letting network operators manage energy infrastructure at a granular level.
AI is also helping to offset its own energy demands on data centres. The IEA projects that global data center electricity use is expected to more than double by 2030, reaching about 945 TWh. AI is supporting Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS), which deploys systems to capture excess carbon emitted from energy-intensive factories and processing plants.
3. AI in manufacturing
AI is handling both heavy-lifting duties and intelligent operations in manufacturing.
Our high-octane, globally competitive markets require manufacturing and production processes to be as streamlined as possible. Customers’ expectations around the quality of goods are growing fast, and this pressure is falling on businesses and manufacturers alike.
AI in manufacturing examples, such as predictive maintenance, study factory machinery and equipment data to pinpoint future breakdowns. For troubleshooters, this presents a chance to proactively maintain equipment health instead of reacting to problems after they’ve happened.
Seemingly insignificant, repeated system errors caught by AI suggest underlying issues, helping engineers hone in on preventative actions that ultimately mitigate surprise repair costs.
Preventative and predictive maintenance may even involve AI cobots, which carry out critical tasks alongside humans on the factory floor.
4. AI in healthcare
The need for adequate healthcare systems spans society. These necessities, however, have long gone unaddressed, with the consequences now becoming clear.
The WHO projects a shortage of 11 million health workers by 2030, with gaps concentrated in low and lower-middle-income countries. AI has proven itself in handling core healthcare functions, such as decision support, disease diagnosis, X-ray analysis, and automating administrative tasks.
AI in healthcare examples include cancer detection through imaging, virtual assistants for patient intake, and predictive tools that identify high-risk patients for early intervention.
Cancer patients can receive personalized oncology care through AI models that carefully design care programs to deliver highly individualized patient experiences.
Beyond these capabilities, AI presents a huge arena for innovation in the life sciences, with the research and development of new drugs and medicinal discoveries being fast-tracked.
For example, Google DeepMind’s AlphaFold2 was able to predict 3D protein structures from amino acid sequences with pinpoint accuracy. It solved this by training neural networks on known structures and learning spatial folding patterns.
5. AI in education
Education processes have advanced understanding and exploration in every single field. This includes the centuries-long technical and IT academia that led to modern AI.
Today, AI is returning the favor, upending firmly held norms in educational spaces. AI in education examples show how intelligent systems are quietly reshaping how students learn, how teachers support them, and how institutions manage learning at scale.
Adaptive AI learning platforms are enabling highly individualized student experiences. They are swapping out one-size-fits-all strategies for multi-pronged ones that evolve intelligently.
AI can observe students’ past and real-time performance, adjusting lesson content on the fly. AI-enabled intelligent tutoring can now design finely tuned lesson plans bespoke to each student, refocusing teachers’ efforts towards more holistic support.
AR, VR, and other extended reality (XR) technologies will merge physical and virtual learning, utilizing AI as its foundation. Students experience an entirely new realm with AI supporting 3D interactive lessons that cleverly merge knowledge with gamification.
6. AI in retail
Despite pandemic-induced fears of a decline in physical retail stores, the retail sector is still growing strong.
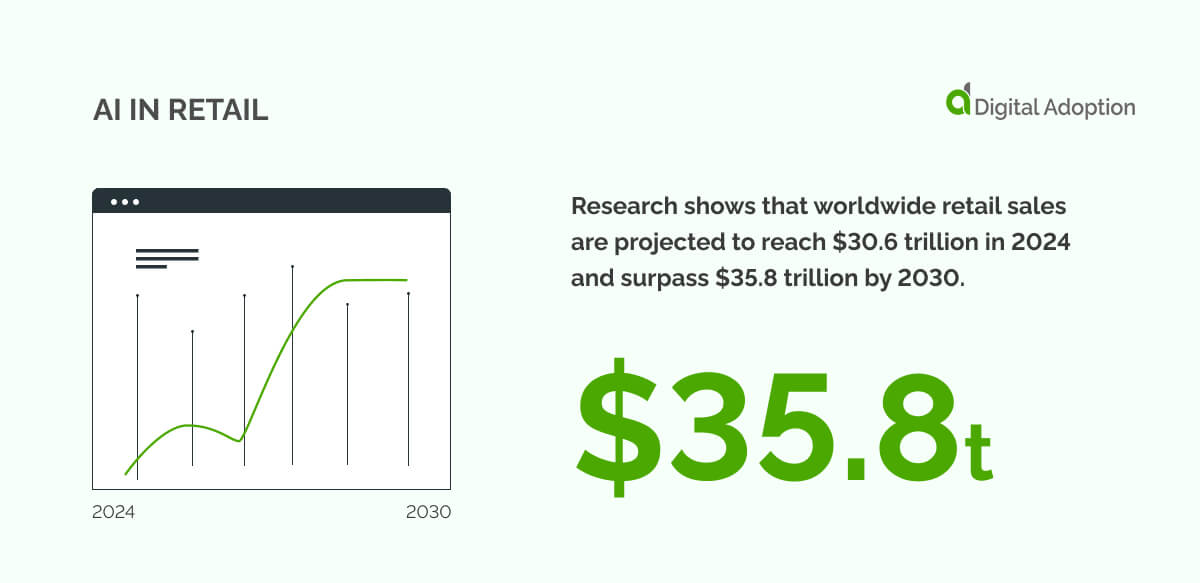
The race to meet constantly shifting consumer demands, however, continues to intensify, and AI presents a chance to bridge that gap.
AI in retail examples show how technologies like recommendation engines, dynamic pricing, and virtual try-ons are changing the way people shop. These tools turn static shopping experiences into immersive, engaging sessions that feel unique to every shopper.
The race to meet constantly shifting consumer demands, however, continues to intensify, and AI presents a chance to bridge that gap. Now, AI can turn static shopping experiences into immersive, engaging sessions that feel unique to every shopper.
SMART stores now host retail robots that fulfill both customer-facing and back-office tasks. AI retail bots can roam stores and engage with customers, using computer vision to recognize customers and deliver contextual help.
With permission, it can access customer activity data to learn shoppers’ buying behaviours and product preferences. Highly specific recommendations can then be made based on this information, bringing the customer closer to their ideal purchase.
7. AI in eCommerce
The speed of online transactions and engaging user experiences have made eCommerce a major force in global retail.
More people are shopping online. Global eCommerce sales are expected to pass $4.3 trillion by 2025. The internet has fueled this growth. For many, it’s now the main way to shop.
AI in eCommerce examples show how online stores are becoming increasingly smarter. These systems learn from each visit to improve search results and simplify delivery.
AI also boosts product tracking, inventory, and even new business models. For instance, AI monitors stock levels, tracks fashion trends, and matches them with customer segments to trigger targeted restocks.
Inventory management is now automated. AI uses robots with computer vision and IoT sensors to move, store, and account for all items. Manual inspections are no longer needed.
8. AI in logistics and supply chain
Industries like retail, e-commerce, healthcare, and manufacturing rely on fast logistics and supply chains.
Clothes, electronics, raw materials, and medical equipment move through global networks daily. A single disruption can halt this flow, causing delays, losses, or life-threatening risks.
AI in logistics and supply chain examples involve enhancing end-to-end network intelligence and supply chain transparency among more. AI can reign in siloed processes across interdependent global supply chains, monitoring and managing operations across network nodes. From orchestrating flow paths, greenlighting suppliers, and making automated system updates.
AI theft response uses CV, IoT sensors, and robots to track inventory in detail. For last-mile delivery, AI adjusts routes in real time, guiding drivers to the fastest paths.
9. AI in insurance
Insurance claims are becoming highly individualised thanks to AI. In the past, claims were reviewed by hand using static data. This data was often outdated and didn’t reflect current conditions. Health records, credit scores, or income reports were used, even if they had changed.
Today, AI in insurance examples involves using real-time data to improve accuracy. This lowers the chance of errors and makes sure payouts better match people’s needs.
In life insurance, AI can even pull health info from fitness apps and wearables. It reads things like age, lifestyle, and medical history to create fairer policies.
In manufacturing, AI tracks equipment health. It helps mitigate breakdowns and updates insurance by monitoring asset risks in real-time.
10. AI in HR
HR teams are constantly tasked with sourcing talent, onboarding new hires, handling complaints, and managing payroll.
AI is modernizing processes that are long overdue for an upgrade. AI in HR examples highlight how it scales candidate sourcing and talent acquisition far more efficiently than manual methods. With access to recruiter and candidate data across platforms, it scans thousands of resumes, searching for keywords and terms that match people to roles.
In workforce planning, AI also analyses project success rates, missed deadlines, and bottlenecks to forecast hiring needs.
Intuitive AI agents handle employee queries anytime. Sentiment analysis helps detect burnout, dips in morale, and workplace tension.
11. AI in cybersecurity
The emphasis on cybersecurity over AI systems can not be overstated. AI uses large amounts of personal and sensitive data to build its future understanding and abilities. If these systems are breached, the harm could be serious and long-lasting.
When done right, AI can augment cybersecurity needs with innovations once thought impossible. AI in cybersecurity examples show how it can stop threats as they happen by watching system activity nonstop.
This includes spotting unusual software changes or user behavior, like logins from new locations or at odd times.
If it detects something odd (like phishing or unauthorized log-ins), it raises the alarm and isolates the threat. It learns from these events to inform stronger threat responses and detection down the line.
12. AI in marketing and sales
Shifting market trends, customer expectations, and competitor pressures are strong-handing marketing and sales teams to brainstorm innovative success strategies.
AI in marketing is easing this pressure. It uses years of customer data to build accurate marketing and sales campaigns to understand their needs and behaviors.
AI tracks buying habits, e.g., past purchases, frequency, and preferences. It also considers age, gender, spending patterns, or whether someone is environmentally conscious. This helps place targeted campaigns in front of the right customer.
Customer interactions shift from static to personal and adaptive. AI can remember and track customers across touchpoints. They also greet users with metrics or suggest items as they browse. Away from product recs, AI assistants can handle refunds, questions, and complaints.
13. AI in IT operations
Our final entry, AI in IT operations examples, shows how intelligent systems are enhancing operational resilience and efficiency across the technology arena. This includes everything from automating routine tasks to detecting system anomalies before they escalate.
The majority of modern industry, from private to public, relies on technology for critical operations. That makes AI a seamless fit for supporting functional strengths.
Machine learning models perform predictive analysis on IT systems and software. They assess live operational data and use past metrics scores. This helps build a real-time view of current and future system performance.
A centralized AI can deploy several agents underneath it. These include monitoring nodes, automated scripts, or embedded models.
Each one checks different systems on the network. This enables AI to predict risk, improve fault detection, and increase uptime across complex digital infrastructure.
Understanding AI risks across industries
The risk landscape is always changing with AI innovations. This makes the design and responsible AI design very important.
Both AI developers and users must follow governance frameworks. These rules help ensure AI is used safely and clearly.
We suggest using the NIST AI Risk Management Framework or the OECD AI Incidents Monitor (AIM) to inform users, businesses, policymakers, and all stakeholders on the proper use of AI.
As industries move towards AI-driven digital transformation, safety is non-negotiable for ensuring both successful and responsible outcomes.
People Also Ask
-
What makes an industry suitable for AI integration?An industry works well with AI when it deals with lots of data and tasks that repeat or are hard to do by hand. AI helps by quickly looking at data and doing tasks automatically. This saves time and reduces mistakes. AI is also becoming very beneficial in industries like retail, healthcare, and manufacturing.
-
How do AI applications scale differently for small businesses vs. enterprises?Small businesses often use AI tools that are ready to go, like chatbots or marketing helpers. These tools are simple to use but might not do everything a big company needs. Large companies build custom AI systems. These systems can handle more data and complex tasks. They can also grow and change as the company does.
-
What privacy or security concerns arise from industrial AI systems?AI handles private data, so if it’s not safe, this info can be stolen or misused. Threat actors can also cause AI to fail or behave badly. That’s why strong security and clear laws are needed to protect data and keep AI working correctly.

 FACT CHECKED
FACT CHECKED![13 AI Examples in Industry [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2025/07/AI-Examples-in-Industry.jpg)







