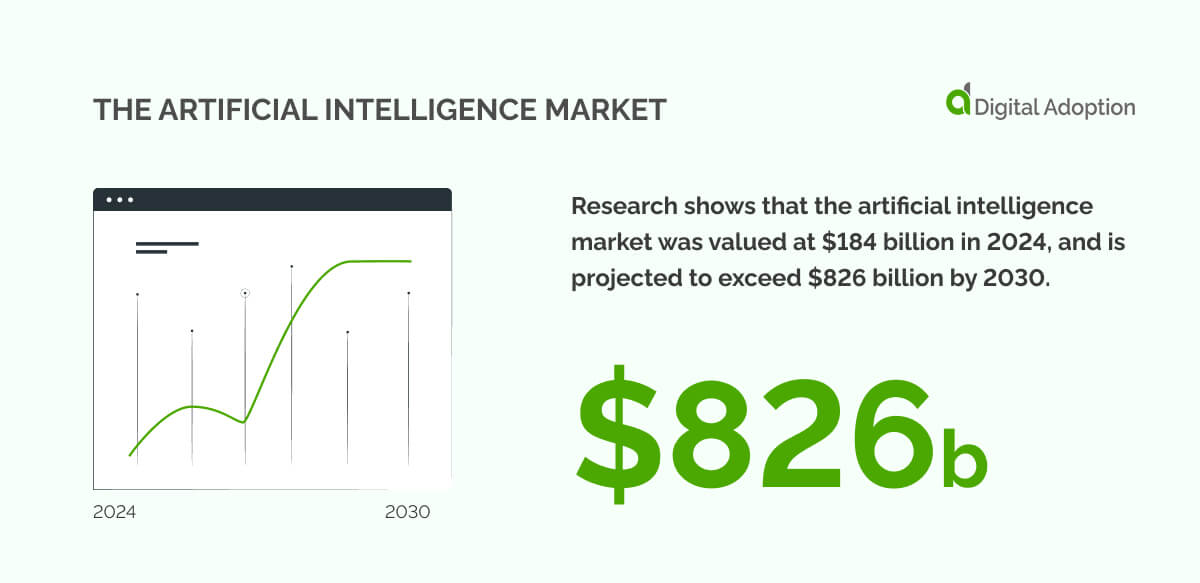
The potential glimpsed through generative AI platforms such as ChatGPT has spurred an expansion of AI in business.
Underpinning a large portion of businesses’ operations are robust logistics and supply chain transformations, which ensure the swift movement of goods and services globally.
If logistics and supply chains are to support these business process transformations, AI adoption becomes essential.
This article will delve into 17 examples of AI in logistics and supply chain management. Explore how AI is augmenting capabilities, from network intelligence and planning to security, compliance, and resilience.
AI in logistics and supply chain examples at a glance:
| AI Technology | Function | Category |
| End-to-end supply chain visibility | Tracks goods and stock across all suppliers and routes | Network intelligence and planning |
| AI-driven material sourcing | Finds cheaper or greener raw materials based on live data | Network intelligence and planning |
| Demand forecasting | Predicts how much of a product will be needed in the future | Network intelligence and planning |
| Supplier risk analysis | Checks suppliers for delays, fraud, or weak finances | Network intelligence and planning |
| Digital twin modeling | Creates a virtual copy of the supply chain to test changes safely | Network intelligence and planning |
| Smart inventory control | Uses sales trends to decide what stock to order or keep | Operational optimization |
| Bottleneck and disruption prediction | Spots weak spots in routes or factories before delays happen | Operational optimization |
| Load optimization | Plans the best way to pack and ship goods | Operational optimization |
| Warehouse system optimization | Organizes where goods go in the warehouse for faster picking | Operational optimization |
| Predictive maintenance | Warns when machines need fixing before they break | Operational optimization |
| Last-mile delivery routing | Plans the best local routes for faster delivery | Operational optimization |
| Automated customs processing | Fills out shipping paperwork using rules and scanned documents | Operational optimization |
| Enhanced theft response | Spots missing items early and sends alerts | Security, compliance, and resilience |
| Embedded sustainability | Tracks emissions, fuel use, and packaging to cut waste | Security, compliance, and resilience |
| Contract review and vendor negotiation automation | Reads contracts, flags risks, and suggests fair terms | Security, compliance, and resilience |
| AI-enhanced quality control and assurance | Checks items for cracks or defects during production | Security, compliance, and resilience |
| Workplace safety monitoring | Watches for unsafe actions or areas in warehouses | Security, compliance, and resilience |
Network intelligence and planning
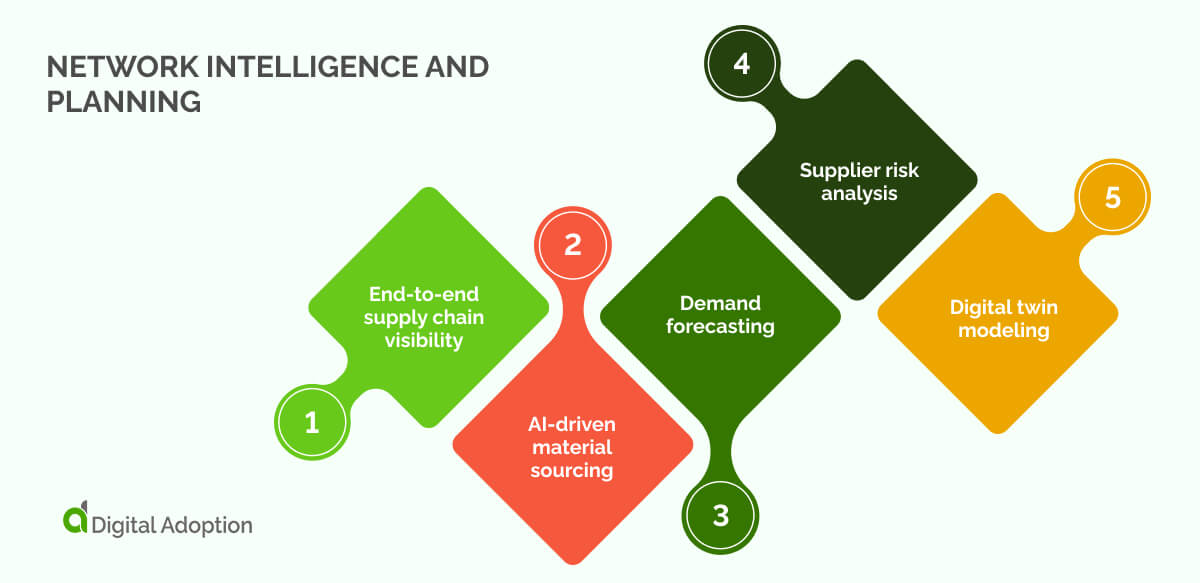
Our first housing category focuses on how AI is increasing visibility and transparency across networks and supply chains, from design, forecasting, sourcing, and risk analysis.
It helps businesses respond faster to changes, reduce blind spots, and make smarter decisions across the entire supply chain.
End-to-end supply chain visibility
Achieving end-to-end visibility across the supply chain is a significant challenge. It requires managing fulfillment networks, flow paths, supplier orchestration, and distribution nodes simultaneously.
Water-tight manual processes have long supported logistics and supply-chain operations, especially across interdependent global supply chains. AI can facilitate transparency over the entire network, restructuring each moving part informed by a single source of truth.
AI constantly gathers data to enable uninterrupted network updates, providing those in charge of operations, specifically the Chief Supply Chain Officer (CSCO) and the Chief Procurement Officer (CPO), with enhanced control over the entire supply chain.
AI-driven material sourcing
Manual material sourcing hinged on managing data across countless systems, transferring supplier and business-critical information, finding reputable vendors, and checking product quality. These tasks are usually handled by sharp-eyed human procurement teams.
AI can now augment this process end-to-end, from sourcing and securing to forecasting and accurate decision-making. Sourcing semiconductors, for example, AI predicts future supply patterns, forecasting shortages or demand spikes.
AI can also assess material quality using third-party data, supplier reputation, delivery accuracy, ESG ratings, and customer reviews.
Demand forecasting
Reading historical data and real-time data simultaneously enables AI to build a high-level framework for predicting how future events may unfold.
Weighing this many data points while accounting for the many variables involved is nearly impossible for human cognitive functions. AI can assess demand in future supply chains and simulate anomaly events that could disrupt operations.
It considers external impacts (e.g., market or geopolitical shifts) to see how they may affect demand capabilities. In preparation for this, AI can plot alternate strategies to offset demand disruptions.
Supplier risk analysis
Once again, manual, time-heavy processes were used to assess supplier risk. Human teams tracked delays, reviewed audits, checked performance, and flagged transport or production issues. Now, AI lightens the load by scanning the full supplier network for risk.
It tracks performance, delays, routes, and audit scores in real-time. If issues appear, AI can suggest alternate suppliers. ESG and compliance goals can also be met by utilizing AI tracing tools that verify sourcing, origin, labor practices, and environmental impact.
Digital twin modeling
AI is delivering risk-free, practical application testing of logistics and supply chain operations with 3D digital twins.
It brings supply chain setups to life through virtual simulations and 3D copies of real spaces and systems. AI can test high-risk events, like how a nuclear plant would recover from a meltdown.
It combines live sensor data with factory blueprints to build a detailed digital model. This lets teams test risky scenarios safely, without causing damage or disruption in the real world.
Operational optimization
This category focuses on AI examples that enable stronger execution, asset coordination, and flow efficiency within supply chain operations.
Smart inventory control
AI is bringing a god’s-eye view to inventory management, adding smart controls that make operations more reliable.
AI models track inventory across distribution points and plan how assets move between sites as demand shifts. It can follow shipments in motion and work with carriers to handle last-minute changes.
Weighing stock levels against customer types helps direct products to the right locations. Buyers avoid overstocking or running short, and suppliers can adjust before production drops off.
Bottleneck and disruption prediction
The punctuality of shipments, port traffic, freight capacity, production speed, and future sourcing can be measured by AI to predict bottlenecks. Comparing how these factors relate helps AI estimate where problems might happen later.
For example, political unrest in countries that supply precious metals can disrupt parts needed for laptops and smartphones.
AI watches these outside events closely. raising warnings where delays or shortages could affect the supply chain further on.
Load optimization
Transport and load logistics can be fine-tuned with AI. Countless shipments circle the globe, expected to be on time, optimized, and cost-efficient.
Freight companies use strict calculations to manage space and weight for huge volumes. AI automates these calculations, tracking storage and flow more precisely than humans.
It weighs item size, weight, and delivery priorities to fit goods into trucks or containers. When delays occur, AI adjusts plans to avoid overloading and meet regulations, cutting fuel use and transport costs.
Warehouse system optimization
Overseeing and optimizing warehouse operations is now possible with AI. Checking stock levels once meant walking the floor, logging data by hand, and updating separate systems.
These checks also had to match up with equipment needs and warehouse layout to avoid delays. AI replaces fragmented tasks with a single view of what’s where, what’s needed, and what’s next.
It uses warehouse sensors to map physical spaces, track item flows, and adjust schedules. If orders spike or equipment fails, AI reshuffles routes, restocks faster, and reduces wait times across the warehouse settings.
Predictive maintenance
One of AI’s most exciting prospects is its ability to forecast future events by inferring intricate patterns from data.
The infrastructure underpinning supply chains and logistics is immense, with software, hardware, and freight carriers moving huge quantities across road, rail, air, and sea. When something fails, it can block the entire chain.
AI can track warehouse systems, factory equipment, and freight infrastructure. It compares service timelines, fault logs, and machine output rates to predict breakdowns.
This turns maintenance into a proactive effort rather than a reactive one, allowing teams to rectify asset failures and extend their lifecycle.
Last-mile delivery routing
Fixed and pre-planned delivery routing fails to adapt to the shifting conditions of the last mile. Traffic lights, accidents, roadworks, and congestion all disrupt urban delivery flow.
AI’s live surveillance can keep pace, pulling GPS and satellite data to map road conditions in context. It compares travel times from past and current routes to pick the fastest option.
AI can even reorganize drop-offs mid-route and flag problem areas down the road, helping delivery fleets stay accurate and responsive in dense, unpredictable zones.
Automated customs processing
Cross-border shipping often slows down at customs due to the security regulations in place.
AI automates key steps, such as document checks, compliance verification, and tariff classification, reducing delays and human-prone mistakes.
This facilitates more efficient border clearances and faster deliveries. It also helps companies stay compliant with changing regulations across international territories.
For global logistics, automated customs processing eliminates friction and reduces the time spent on paperwork, while ensuring goods are moved safely and lawfully.
Security, compliance, and resilience
The final category is security, compliance, and resilience, focusing on minimizing risk, ensuring regulatory alignment, and strengthening supply chain stability under pressure.
It highlights how AI can preempt threats, automate compliance, and maintain business and customer continuity during unexpected events.
Enhanced theft response
Luckily, AI is strengthening theft responses, having a constant pulse on supply chain, distribution, and transport processes. It can monitor the movement of goods and flow paths across the entire chain, honing in on any actions that deviate outside normal parameters.
AI alerts nearby authorities the moment a threat is detected. Everyone involved is notified in real-time. Geofencing adds another layer—drawing invisible lines around high-risk zones. If a truck crosses out of bounds, AI reacts instantly to that breach.
Embedded sustainability
Tracking the environmental impact of deliveries helps companies lower their ecological footprint and meet ESG standards.
Tracking emissions from each delivery and suggesting routes that use less fuel is helping embed sustainability in the sector. It evaluates packaging options and flags suppliers with poor environmental records, guiding more eco-friendly choices.
AI also forecasts demand to avoid excess shipments and waste. These insights make it easier to balance timely deliveries with reducing environmental impact. Sustainability becomes part of daily operations, not a greenwashing attempt, keeping logistics mindful of both planet and performance.
Contract review and vendor negotiation automation
Contract reviews used to involve sorting through stacks of paper, checking signatures by eye, and auto-flagging issues.
AI now brings structure to that process. Image recognition reads scanned contracts, identifying handwritten signatures, stamps, and embedded terms. Intelligent document processing then extracts key details, linking them to supplier records and delivery terms.
From there, NLP scans for risks, missed clauses, or inconsistencies. When it comes to negotiation, AI can reference past vendor outcomes and run comparisons to suggest fair pricing or term revisions.
AI-enhanced quality control and assurance
High-tech cameras and sensors, integrated with quality management system software, inspect products at various points throughout the production process.
They check for imperfections, odd colors, or damaged parts. The system studies what a perfect product looks like, and then improves its accuracy over time. Each check helps catch defects early before they move further down the chain.
Fewer faulty items reach customers, which cuts down returns and keeps standards consistent. It also helps companies track where quality slips and fix problems faster across the supply chain.
Workplace safety monitoring
Sensors and smart office technology watch for unsafe movements, like lifting something the wrong way or walking into a restricted zone.
When something risky happens, the system sends out alerts right away. It also studies past safety events to spot patterns and suggest safer habits. Over time, it learns what works and what doesn’t.
This helps keep workers safer in busy warehouse spaces and lowers the chances of sudden delays caused by accidents or injury.
Driving disruption and growth in AI in logistics and supply chain
The technology powering logistics and supply chains often goes unnoticed.
Yet, it runs the world behind the scenes, ensuring the timely delivery of goods that impact global trade and business outcomes.
The introduction of AI promises major digital disruption, driving a new wave of digital transformation across these industries. As this technology develops, strong AI ethics and risk assessments will be essential to ensure quality and trust.
“AI is a moving target,” says Chris Caplice, executive director of the MIT Center for Transportation and Logistics. This shows how quickly AI evolves, requiring constant attention and digital adaptation.
With the market expected to exceed $41 billion by 2030, the coming years will be compelling as logistics and supply chains push the boundaries of what’s possible.
People Also Ask
-
What are the benefits of AI in logistics and supply chains?AI helps track goods, shorten delivery times, and avoid stock issues. It finds patterns in past orders to forecast demand and adjust supply. It can spot delays early and suggest better routes. AI also checks fuel use, warehouse space, and loading patterns to cut waste.
-
What are the risks of AI in logistics and supply chains?Bad data or flawed models can lead to wrong choices. Overreliance on automation can limit human judgment. Privacy rules can be ignored. AI errors can harm supplier ties or delay goods. Hacked systems also risk large-scale disruption.
-
How to prepare supply chains and logistics for AI?Clean data and clear records are the first step. Train staff to use AI tools and question results. Test before scaling. Set rules to guide use and review systems often to stay safe and up to date.

 FACT CHECKED
FACT CHECKED![17 Examples of AI in logistics and supply chain [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2025/07/17-Examples-of-AI-in-logistics-and-supply-chain-2025-img.jpg)







