A Chief Information Officer (CIO) is an employee who manages the personnel, operations, and technologies within an organization’s IT department, ensuring they align with and support business objectives.
As digital capabilities become fundamental to organizations, the CIO is pivotal in steering crucial strategic, technical, and managerial undertakings.
These range from ensuring data security and developing algorithms for business models to enhancing customer experience transformation and utilizing data to address potential challenges and stimulate business expansion.
The scope of the CIO’s responsibilities has broadened over time. They are now integral to determining how technology can be harnessed to fulfill business aims and bolster revenue and profitability.
Nowadays, CIOs spearhead initiatives related to business transformation and oversee large-scale organizational shifts.
In the face of emerging technologies and the rapid pace of digital transformation, CIOs have cultivated competencies that surpass conventional tech management.
Once you read this article, you will learn more about:
- The meaning of CIO, what the role involves, and why you need one for your business
- The qualifications and skills required to become a CIO
- The salary you can expect to get as a CIO
- The steps you need to take to get a CIO position
- Who in the organization a CIO works with
- The difference between a CIO, CDO, and CTO
- The future of a CIO role
CIO Meaning
The Chief Information Officer (CIO), also referred to as the Chief Digital Information Officer (CDIO) or Information Technology (IT) Director, is a senior executive title often designated to the highest-ranking individual in a company responsible for managing information technology and computer systems to align with the organization’s business strategy.
Typically, the CIO reports to the Chief Executive Officer (CEO). However, they may also be accountable to the Chief Operating Officer (COO) or Chief Financial Officer (CFO). In military settings, the CIO answers to the commanding officer.
What Is The Role Of A CIO?
Any organization’s Chief Information Officer (CIO) holds multiple pivotal roles. Primarily, a CIO acts as a transformational business leader. They make critical executive choices, such as selecting IT equipment vendors or developing novel IT systems.
In their leadership capacity, CIOs also guide and steer the direction of their organization’s workforce. Recruitment also falls under the CIO’s purview, emphasizing the need for them to identify and cultivate top-tier talent actively.
The CIO must design their organization’s Information and Communication Technology (ICT) strategy and policy. While the ICT strategy encompasses future planning, procurement, and organizational standards, CIOs must also use IT to enhance business operations.
Lately, with the growing demand from customers for digital services, CIOs are increasingly involved in developing customer-centric products. CIOs have taken on more product-driven roles because digital offerings are now integral to customer relationships.
Need For A CIO
CIOs are pivotal in businesses leveraging technology and data, as they act as the crucial link between business requirements, user necessities, and the information and communication technology (ICT) tools implemented.
Additionally, CIOs have taken on a heightened role in optimizing costs and enhancing profitability through ICT deployment. They also safeguard organizations by instituting IT safeguards and strategizing for potential IT disaster recovery.
In short, you need a CIO to bridge the divide between IT-centric and non-IT roles and foster cohesive collaboration across departments.
CIO Job Description And Duties
The role of CIOs can differ considerably based on the specific organization, industry, and geographical location in which they operate.
But, In most entities, the main goal of a CIO is to oversee the IT infrastructure and computer systems that align with and support business goals and objectives. Their primary duties revolve around innovating, collaborating, managing the IT budget, measuring digital transformation, and inspiring their teams.
The key responsibilities of a CIO typically encompass the following:
- Leading the IT team and setting departmental objectives;
- Formulating and managing the IT budget;
- Strategizing, implementing, and upkeeping IT systems and operations;
- Addressing the organization’s software development requirements;
- Crafting IT policies, guidelines, and best practices;
- Keeping abreast of the latest IT trends and breakthrough technologies;
- Implementing IT best practices throughout the enterprise;
- Guaranteeing that IT strategies and procedures are in sync with overarching organizational objectives;
- Managing relationships with external vendors, contractors, and service providers;
- Communicating to the board and other top executives the potential advantages and risks of forthcoming IT-centric projects.
What Qualifications Does A CIO Need?
Typically, businesses expect a CIO to qualify in an area related to computer science, computer information systems, IT management, or database administration.
Possessing a master’s degree in business administration, coupled with a computer-centric degree, can further equip a CIO to effectively handle strategic planning, development, recruitment, and budgeting from a business perspective.
Important CIO Skills
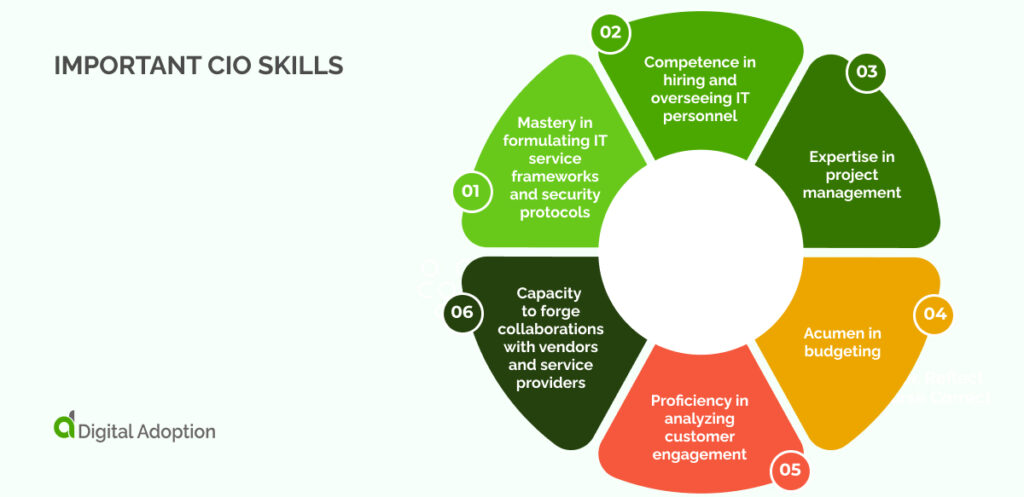
A combination of specific technical know-how and interpersonal abilities is essential to thrive as a CIO. Understanding the inner workings of a business is crucial, as even a CIO interview will seek to understand your current knowledge about the company’s operations at every level, including digital transformation interview questions.
Prospective CIOs are expected to possess competencies in two main areas: hard and soft skills. Hard skills are specific, trainable proficiencies essential for a particular role.
Commonly sought-after hard skills for CIO positions include:
- Mastery in formulating IT service frameworks and security protocols;
- Competence in hiring and overseeing IT personnel;
- Expertise in project management;
- Acumen in budgeting;
- Proficiency in analyzing customer engagement and
- Capacity to forge collaborations with vendors and service providers.
On the other hand, soft skills pertain to an individual’s interpersonal aptitudes. Qualities like empathy, optimism, integrity, teamwork, and a sense of humor fall under this category. These traits play a crucial role in one’s leadership and managerial capabilities, which are foundational for a CIO role.
A significant aspect of the CIO’s role involves advocating for technological advancements and the imperative of digital transformation to a company’s leadership and board.
Therefore, stellar communication and interpersonal skills are paramount. These skills foster harmonious interactions with fellow executives and IT teams and bolster overall job performance and future career opportunities.
What Is A CIO Salary?
The compensation for CIOs is continually increasing due to increasing regulatory and reporting requirements.
On the whole, the salary for a CIO can differ based on multiple determinants, such as:
- Educational background
- Professional experience
- Skillset breadth
- Geographical location
- Specific industry
- Nature and scale of the employing organization
While Comparably shows that the salary for a CIO is $217,246, Glassdoor shows that the salary for a CIO is $327,475 as of September 2023. This means that the average wage is about $272,360.5.
How Do You Get A Job As A CIO?
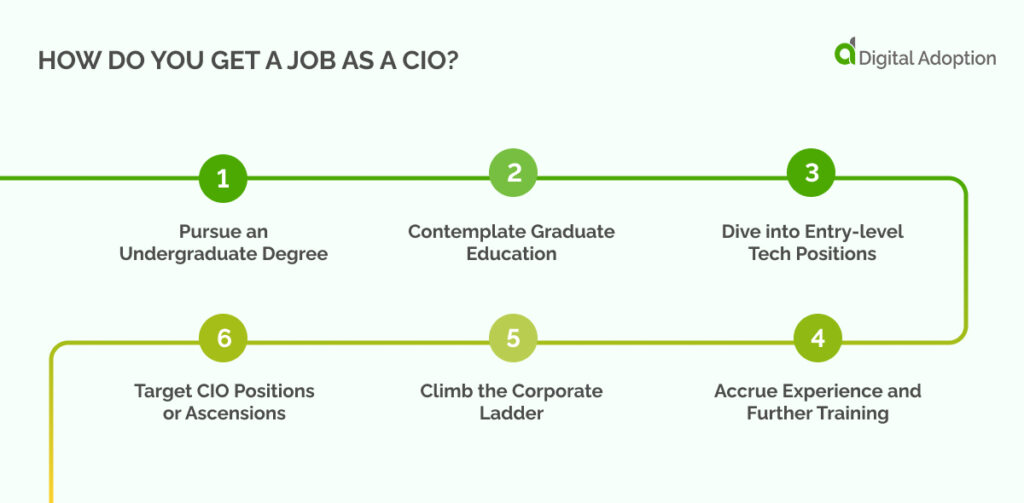
If you’re keen on maximizing your potential in the IT domain, you might be contemplating the path to becoming a chief information officer (CIO).
As CIOs are top-tier executives seasoned in information management, their roles necessitate a comprehensive set of skills and credentials.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to carving a path toward becoming a CIO:
Pursue an Undergraduate Degree
Most CIOs today hold a bachelor’s degree in a tech-centric field. Consider majors like computer science, computer information systems, or database administration. These disciplines impart the foundational technical knowledge pivotal for a promising CIO career. Typically, these degrees span three to four years of full-time study.
Contemplate Graduate Education
With a bachelor’s degree, a graduate degree can further refine your competencies, enhancing your prospects for the CIO role. If your bachelor’s is tech-oriented, balance it with a master’s that offers insights into business and management, such as an MBA. For those already in the workforce, part-time master’s programs can be a viable option.
Dive into Entry-level Tech Positions
Ascending to the CIO’s office demands substantial hands-on experience in IT and tech management. Starting points could be roles like IT specialist or database administrator. These positions offer a platform to hone skills essential for a CIO position.
Accrue Experience and Further Training
As you navigate the tech landscape, focus on enhancing your profile. Seek out advanced certifications, shoulder added responsibilities, and immerse yourself in roles that emphasize management and strategic thinking. Pursue recognized certifications in tech management or consider specialized courses in information management.
Climb the Corporate Ladder
Remember, CIOs are at the heart of the organization’s culture. Hence, a significant tenure in diverse tech roles is a common precursor. Seize opportunities that pave the way for increased responsibilities. Set your sights on roles with job titles like chief technology officer (CTO) as a stepping stone to the CIO designation.
Target CIO Positions or Ascensions
Many achieve the CIO title by climbing the ranks within a single firm, reflecting their dedication and commitment. Staying loyal to one organization can spotlight you when the top seat becomes available.
However, exploring opportunities across various companies can offer rapid advancements. With the proper skill set and experience, applying for external CIO roles can be a strategic move.
Who Does A CIO Work With?
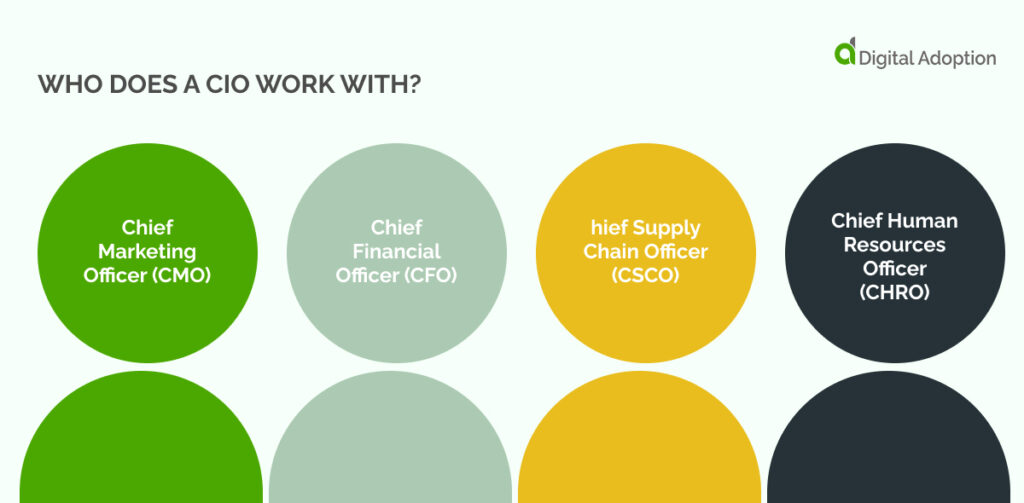
The CIO typically answers to numerous large corporations’ chief executive officers (CEOs). In certain establishments, the CIO is granted a position on the executive committee.
CIOs often collaborate closely with various top-tier executives, such as:
- Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Chief Supply Chain Officer (CSCO)
- Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO)
Additionally, CIOs maintain a synergistic relationship with the Chief Technology Officer (CTO), whose primary focus revolves around developing products catering to customer demands.
The CIO might share overlapping organizational duties with designated Chief Security Officers or Chief Digital Officers.
Difference Between A CIO, CDO, And CTO
The designations of chief information officer (CIO), chief digital officer (CDO), and chief technology officer (CTO) often get intertwined and understood.
Broadly speaking, while CTOs primarily concentrate on the technological aspects, usually customer-oriented ones, CIOs delve deeper into integrative applications within a corporate framework and its governance.
Traditionally, CTOs were seen as harnessing technology to carve out an external competitive edge. However, this definition has expanded to encompass CDOs, who harness contemporary technologies, digital strategies, and data analytics to drive a company’s digital transformation.
Future Of A CIO Role
The Chief Information Officer (CIO) is essential in integrating IT solutions into an organization’s daily functions. This involves supervising computer infrastructure, guiding software development, and safeguarding the company from digital threats.
As remote work became the norm and customer engagements shifted, the emphasis on leveraging IT to optimize business operations, reduce costs, and bolster security intensified.
As part of the executive hierarchy, a CIO should possess a robust understanding of business dynamics, exemplary communication abilities, a flair for strategic foresight, and a deep grasp of the company’s operational intricacies and tech-oriented objectives.
In the future, the CIO’s role is bound to undergo further transformations. They must stay abreast of emerging IT paradigms—notably, the shift towards a service-driven application framework that could supersede legacy enterprise software.
Moreover, the accelerated tempo of technological and business evolution cannot be overlooked. In short, CIOs should channel their efforts toward digital innovations that offer a competitive edge.
In this dynamic environment, adaptability is essential for CIOs. They’ll need to personally harness many competencies from their teams and associates to drive change.
Collaboration with other individuals becomes imperative as roles and responsibilities blur. For CIOs, this might mean transitioning from solely focusing on talent acquisition to emphasizing talent cultivation in-house and via specialized training initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does A CTO Do Vs. A CIO?
A CIO typically oversees an organization’s IT department, ensuring its seamless integration with other divisions within the company.
On the other hand, a CTO is an executive responsible for the development, engineering, and research teams, with a primary focus on enhancing the product lineup.
Is a CIO a CEO?
While CEOs lead an organization, the CIOs spearhead digital transformation initiatives. In forward-thinking companies, CIOs have broader responsibilities beyond digital strategy to encompass other IT-related functions.
Is A CIO Higher Than A Director?
Although a CIO can handle duties similar to those of an IT Director, their primary role is to oversee the organization’s strategic technology planning. Typically, the CIO reports directly to the CEO.




![18 Examples of AI in Finance [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/18-Examples-of-AI-in-Finance-2025-300x146.jpg)
![14 Examples of AI in Manufacturing [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/14-Examples-of-AI-in-Manufacturing-2025-300x146.jpg)
![29 Examples of AI in Education [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/29-Examples-of-AI-in-Education-2025-300x146.jpg)
![15 Examples of AI in Retail [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/15-Examples-of-AI-in-Retail-2025-300x146.jpg)
![13 Examples of AI in Healthcare [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/AI-in-healthcare-examples-300x146.jpg)


![18 Examples of AI in Finance [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/18-Examples-of-AI-in-Finance-2025.jpg)
![14 Examples of AI in Manufacturing [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/14-Examples-of-AI-in-Manufacturing-2025.jpg)
![29 Examples of AI in Education [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/29-Examples-of-AI-in-Education-2025.jpg)