In the world of modern business, technology adoption is a means to build competitive advantage. However, the challenge often lies in how technology and digital innovation are welcomed by the people who are meant to use them.
This is where the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) comes into play. It provides a framework to understand why users accept or reject technology.
Research shows that TAM can explain up to half of why people decide to use a new system. In other words, nearly 50% of the time, whether a tool is adopted depends on how useful and easy to use employees believe it is.
Many organizations use TAM questionnaires to understand how people feel about new systems. These surveys reveal whether employees see a tool as helpful or easy to use, giving leaders the insight to improve adoption.
This article explores how Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) questionnaires support digital adoption by helping businesses gauge user attitudes and refine strategies to ensure new technologies are embraced across the workforce.
- What is the Technology Acceptance Model?
- Why use a Technology Acceptance Model Questionnaire?
- How does the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) work?
- What are the different stages within the user acceptance process?
- How to design a Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) questionnaire
- What are the benefits of using a Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) questionnaire?
- What are the challenges of using a Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) questionnaire?
- Technology Acceptance Model Questionnaire tips
- How can TAM questionnaires impact organizational ROI and digital adoption?
- People Also Ask
What is the Technology Acceptance Model?
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is a framework for understanding why people choose to use or avoid new technology at work.
It focuses on two simple ideas. First, people are more likely to use a system if they believe it will make their job easier or help them perform better.
Second, they are more open to it if they believe it will be easy to use and not require much effort to learn. Together, these two beliefs shape whether a new tool becomes part of daily work or gets ignored.
TAM also helps businesses look beyond the technology itself and focus on the people using it.
Firms use it to understand how employees respond to new digital tools and where resistance might occur. It also helps leaders plan better rollouts and guide people through digital transformation and adoption.
Why use a Technology Acceptance Model Questionnaire?
Businesses use a Technology Acceptance Model questionnaire to understand how employees feel about new systems before and after they’re introduced.
It helps them measure whether people find a tool useful or easy to use, with the results revealing how confident employees feel about learning and applying new technology.
Leaders use this insight to identify pain points such as poor design or lack of training. It also shows whether communication around the change is clear or confusing. The data then helps shape rollout plans that feel practical.
Enterprises aware of their setbacks can pivot and adjust the process instead of blaming the users. Put simply, TAM questionnaires turn employee opinions into clear insights and give leaders concrete guidance to act on.
Over time, adoption rates improve, and a culture is created that’s more open to digital change.
How does the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) work?
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) can seem complex from the standpoint of theory, but when broken down, it’s relatively straightforward.
The TAM looks at how people’s beliefs about a technology shape their willingness to adopt and actually use it. These beliefs are guided by specific factors that determine how people perceive and interact with the technology.
According to ScienceDirect, two primary factors influence this decision:
- Perceived usefulness (PU): How much a person thinks a system will help them perform their job better.
- Perceived ease of use (PEOU): How simple and effortless a person expects it will be to use the system.
To see how widely a new technology is being used, businesses calculate the technology adoption rate. This shows the percentage of people who could use the system and have actually started using it.
The formula is straightforward:
- Technology Adoption Rate (%) = (Number of users who adopted the technology ÷ Total number of potential users) × 100
These perceptions then affect three key outcomes in how people use the technology:
- Attitude Toward Using (ATU): How someone truly feels about a system and whether it excites, frustrates, or motivates them, which shapes their willingness to engage.
- Behavioral Intention to Use (BI): The conscious choice to try or avoid a tool, reflecting the mental commitment before any action is taken.
- Actual System Use (AU): What happens in reality, including the frequency and manner in which people interact with the technology during their work.
What are the different stages within the user acceptance process?
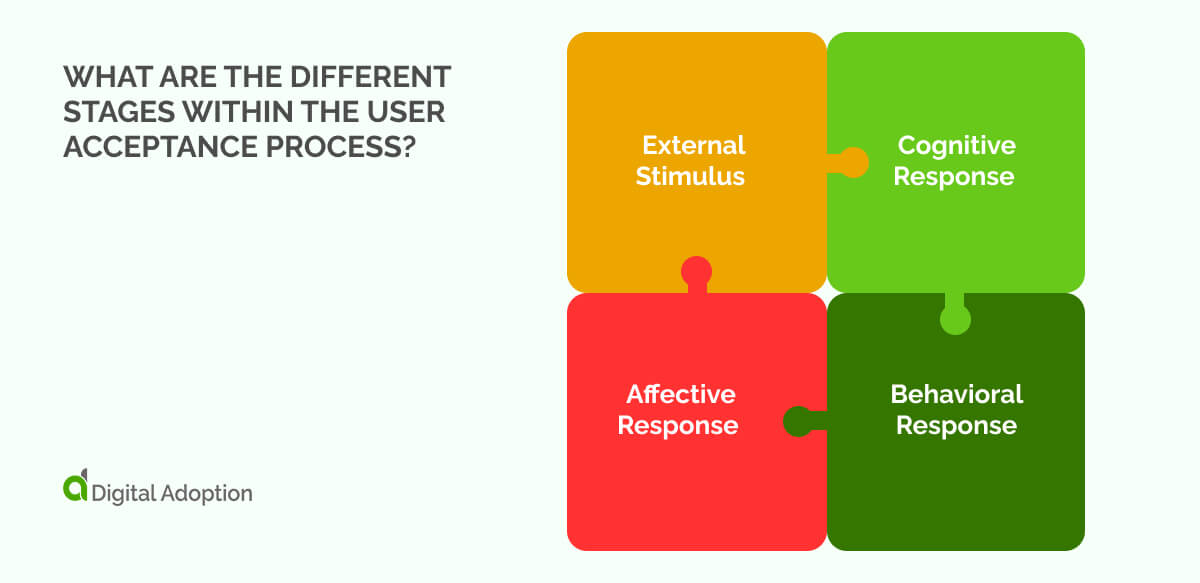
Understanding how people move from first hearing about a technology to fully using it helps explain why some tools succeed and others fail.
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) breaks this journey into distinct stages that show how beliefs and intentions lead to actual use. These are the different stages within the user acceptance process:
External Stimulus
Attention is captured by something outside the user’s control. It might be a notification, a coworker’s tip, or a sudden pop-up. The technology interrupts routine thought and demands notice. Curiosity naturally sparks, creating awareness. This stage sets the scene and, with the tool already in the user’s mind, prompts initial reflection on its relevance and potential impact.
Cognitive Response
The user thinks critically about the technology. Will it save time or add effort? Mental simulations weigh tasks, benefits, and effort. Judgments form around usefulness and simplicity, with logic dominating and guiding initial willingness. Users can decide whether exploring the system is worthwhile. In this stage, cognitive response translates external exposure into an informed opinion or expectation.
Affective Response
Emotions can color perception at this stage. Excitement, frustration, pride, or doubt creep in and influence openness. Positive experiences can reinforce confidence and encourage engagement, while glitches often create hesitation. Feelings are as critical as reasoning at this point, shaping motivation to continue. At this point, users begin forming an emotional attachment, determining whether curiosity turns into genuine interest or passive avoidance.
Behavioral Response
In the last stage, the user takes measurable action. They log in, follow new digital workflows, experiment, and repeat interactions. Habits emerge, embedding the technology into daily routines. By now, adoption has become visible and consistent. This final stage confirms whether earlier perceptions successfully guided behavior, turning potential into concrete engagement.
TAM questionnaires capture these beliefs, emotions, and actions, giving businesses measurable insight into how users perceive and adopt new technology.
How to design a Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) questionnaire
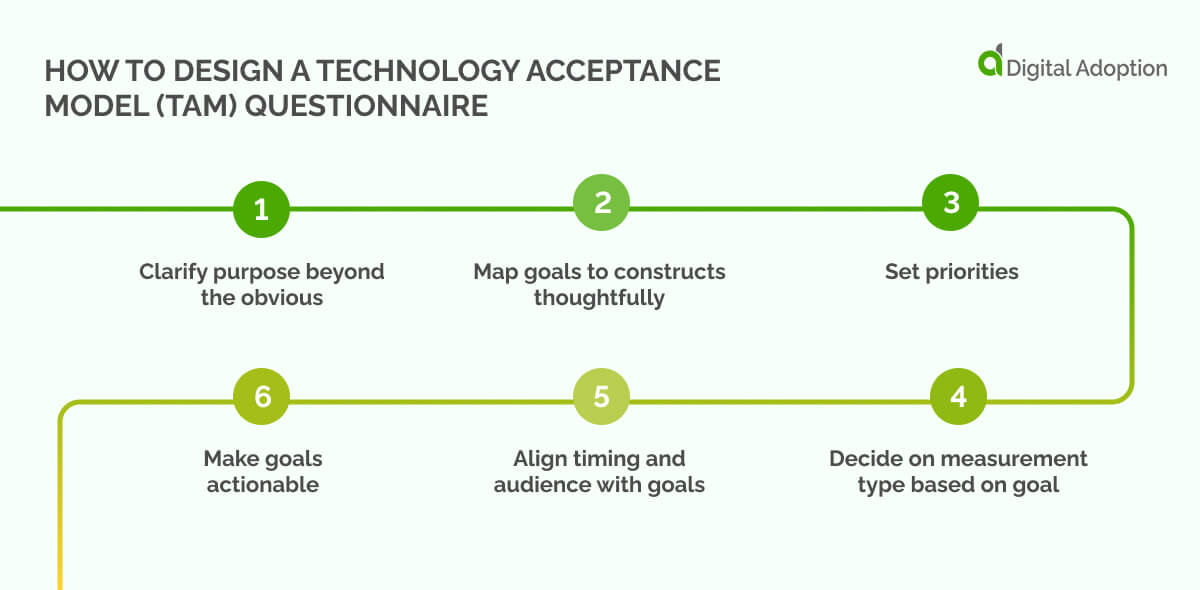
Designing a TAM questionnaire can seem overwhelming at first. We’ve broken down the complexities into six easy-to-follow steps:
Step 1: Clarify purpose beyond the obvious
Don’t just ask “Is this useful?” or “Is it easy to use?” Instead, define measurable outcomes tied to business objectives. Examples include:
- Identifying bottlenecks in workflow adoption.
- Measuring which features drive productivity or satisfaction.
- Predicting which teams or roles may resist adoption.
Frame your goals in terms of decisions you can act on. For instance, instead of “Do employees like the system?” ask “Which specific tasks do employees believe this system will speed up or improve?” This links PU directly to performance outcomes.
Step 2: Map goals to constructs thoughtfully
Once you know your purpose, assign questions to each TAM construct strategically. This includes:
- PU: Focus on task-specific benefits and avoid generic statements. Use statements like “This tool reduces the time I spend on report generation.”
- PEOU: Include contextual ease measures. Ask, “I can complete my daily workflow without assistance from others,” instead of the abstract “easy to use.”
- BI: Explore real-world intent, not just hypothetical willingness. Ask, “I intend to use this tool for at least 50% of my daily tasks within the next month.”
Step 3: Set priorities
You don’t need dozens of questions for every construct. Choose 3–5 high-impact items per construct that give actionable insight. Then, rank questions by decision relevance and not survey completeness. This ensures the questionnaire is concise, keeps engagement high, and focuses on the data that leaders can act upon.
Step 4: Decide on measurement type based on goal
This is important because the way you measure perceptions directly affects the clarity and usefulness of the insights.
Choose the method that best aligns with the type of information you need:
- Likert scales capture the strength of belief. Ideal for both PU and PEOU.
- Scenario-based questions link perception to specific tasks, revealing practical barriers.
- Ranking or forced-choice questions highlight which features or issues matter most.
- Open-ended prompts uncover unexpected obstacles or user insights.
Step 5: Align timing and audience with goals
Determine when the survey will provide the most useful data, whether it’s after initial exposure, mid-pilot, or post-launch. Then, tailor questions to audience segments, including roles, tech experience, and department, so responses reveal where adoption strategies should focus.
Step 6: Make goals actionable
Lastly, for each question, define what a high or low score will trigger. For example, low PEOU on a key feature might indicate the need for a training session or UI redesign. Try to ensure that every goal translates directly into a potential intervention or decision.
What are the benefits of using a Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) questionnaire?
Understanding the benefits helps teams grasp why TAM questionnaires matter and how they can shape smoother, more confident tech adoption.
Let’s take a more in-depth look at the benefits of TAM questionnaires:
Aligning technology with business objectives
TAM questionnaires help pinpoint how technology adoption aligns with strategy objectives. Evaluating perceived usefulness and ease of use means businesses can determine if the technology supports digital transformation KPIs, improves productivity, or streamlines ops. This then ensures that digital initiatives contribute directly to organizational success.
Enhancing user-centric decision making
Direct feedback from users gives enterprises a clear view of their experiences and challenges. For example, using data from employee engagement surveys means improved system design and support services. A user-centric approach informs decision-making processes and support services to better meet the needs of users.
Continuous improvement and adaptation
Regularly using TAM questionnaires helps businesses see how people feel about a system and how their views change over time. This steady flow of feedback keeps technology up to date and aligned with what both the business and its users need.
What are the challenges of using a Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) questionnaire?
The difficulty with TAM questionnaires is in how organizations read and act on them. Missteps in design or interpretation can turn useful feedback into misleading signals.
Let’s take a more in-depth look at the challenges of TAM questionnaires:
Low-tech skills among users
Employees often struggle because they lack basic digital literacy, including knowing how to navigate apps, understand interfaces, or trust online tools. When people aren’t supported with training, especially in technology, their responses often reflect frustration rather than recognizing how useful the technology actually is.
Trust, privacy, and security fears
Even before filling out a questionnaire, concerns about data privacy and security weigh heavily. Users fear that their responses or personal information might be misused. This mistrust can skew answers or lead to low response rates, making the data less reliable for understanding true perceptions.
Context & cultural differences skew responses
What feels “easy to use” or “useful” in one group can feel irrelevant or overwhelming in another. In different countries or cultures, people interpret questionnaire items in diverse ways. For example, a way of asking questions that makes sense in the tech department might confuse employees in other divisions.
Technology Acceptance Model Questionnaire tips
We’ve developed the following TAM questionnaire tips to help you build a complete and easy-to-use survey that captures honest employee feedback and drives meaningful insights for technology adoption.
- Keep questions task-focused: Instead of asking, “Is the system easy to use?” ask, “How simple is it to create and approve a purchase order in this system?” This shows exactly where employees experience friction.
- Avoid jargon entirely: Replace phrases like “system interoperability” with plain language: “Does this tool work smoothly with the other software you use daily?” Everyone can understand that instantly.
- Test with a small group first: Send the questionnaire to one department first. Notice if staff skip questions or ask for clarifications. Adjust wording before a company-wide rollout to avoid confusion.
- Limit questionnaire length: Focus on 10–12 high-value questions rather than 30. Employees are more likely to complete a short form, and the answers tend to be more thoughtful.
- Include context for each question: Add a line like, “Your feedback will help us improve the workflow in this tool,” so employees see how their answers will influence real decisions.
How can TAM questionnaires impact organizational ROI and digital adoption?
A TAM questionnaire reveals how employees actually use new technology. It identifies what works well, what causes employee frustration, and where adoption is slowing down.
Leaders can use these insights to adjust systems, processes, and training. When improvements are made, employees engage more naturally with digital tools.
Greater engagement leads to smoother workflows and quicker adoption across the organization. Then, as adoption spreads, tasks become more efficient and time is no longer wasted.
This efficiency translates into measurable digital transformation ROI, showing how well technology investments are paying off and highlighting areas where further improvements can boost employee satisfaction.
Regular use of TAM questionnaires keeps feedback current and ensures any new tools introduced stay relevant.
People Also Ask
-
What are the methods for measuring TAM beyond questionnaires?Beyond questionnaires, TAM can be measured using system usage logs and tracking how often employees interact with a tool. Interviews and focus groups also provide context behind behaviors. They usually reveal why users act a certain way. A/B testing and pilot programs can be a great way to show adoption patterns, connecting perceptions to real-world usage.
-
What are the real-world applications of TAM?TAM is widely used in enterprises to guide software rollouts, digital workflows, and productivity tools. It helps teams anticipate resistance and prioritize improvements. From homegrown CRM adoption to internal collaboration platforms, TAM informs decisions that accelerate digital adoption across departments.
-
How does low digital literacy among employees impact TAM results?When employees struggle with basic digital skills, their feedback may reflect confusion rather than honest opinion. Low digital literacy can understate a tool’s usefulness or ease of use, leading leaders to misinterpret adoption barriers. Recognizing skill gaps ensures TAM results drive practical improvements rather than misleading conclusions.

 FACT CHECKED
FACT CHECKED







