New working models are becoming more flexible. This means many employees can now work from almost anywhere–whether they’re on the go, at home, or in a traditional office setting
Research by MDPI shows that more than 50% of all workers switched to working from home during the pandemic. This was especially true for knowledge workers. Particularly those who do office jobs on computers, like those in IT, communications, and finance.
More and more employees are bringing their own devices to work. This makes it important for companies to have clear rules about BYOD. These rules help prevent people from using devices that haven’t been approved.
Implementing BYOD programs can boost employee productivity and save companies money on equipment. However, companies need the right security in place. This will help them become digitally proficient and try new things safely.
This article will explore the concept of BYOD, how it works, along with its benefits and challenges. We’ll also share how to enact policies that help maximize BYOD’s advantages while mitigating potential risks.
What is Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)?
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) lets employees use their own phones, tablets, and laptops for work.
Policies like BYOD make device management easy in the workplace. This means employees don’t need separate devices for work and personal life.
These policies let employees use approved technology at work. They can access the company’s network, apps, and important data. However, using personal devices can be risky for companies that store sensitive information. That’s why strong security rules are needed to fight off cyberattacks and keep important information safe.
According to a Bitglass report, 82% of organizations actively embrace BYOD to varying degrees. However, 30% of these organizations face a big challenge–concerns about information security make it hard for them to fully adopt BYOD.
How does BYOD work?
BYOD programs need clear rules about what employees can and can’t do with technology at work. These rules are important in today’s world. Employees often want to use their phones, tablets, and laptops to get their jobs done.
BYOD policies are formal documents that both the company and employees agree to. They clearly outline how employees can use personal devices within the workplace. The company grants certain permissions to employees who follow the BYOD policy. They can connect to the company’s network, access important applications, and work with sensitive data.
There are a few ways employees can leave companies open to attack. This includes using weak passwords, and not being careful when using devices that aren’t protected or approved. These weaknesses are exactly what threat actors (hackers) look to exploit.
Verizon reports that 74% of data breaches involve human mistakes. This includes falling for social engineering attacks, simple errors, or misusing company systems.
Any BYOD program needs strong security. This will help protect against cyberattacks, data leaks, and unauthorized access.
What are the most important aspects of BYOD?
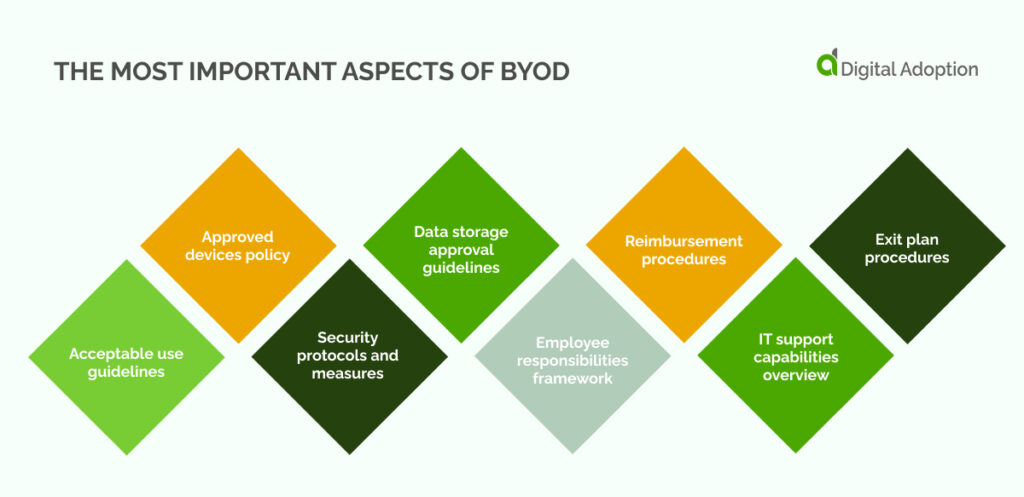
The most important parts of a BYOD policy that find the right balance between workplace flexibility, security, and accountability. They include:
Acceptable use guidelines
A BYOD policy should clearly set forth acceptable use guidelines. This includes telling employees exactly how to use their devices and setting any limits or restrictions.
Approved devices policy
Creating a good BYOD policy is knowing what devices employees will use and what they’ll use them for. It should clearly list the devices employees can use (like specific phone or laptop models). This ensures that all devices work with the company’s systems and meet security standards.
Security protocols and measures
The policy must detail specific security rules and steps that focus on keeping data safe. This includes password requirements and how information should be encrypted. It also includes other ways to protect sensitive data, such as setting up a timed auto-lock or using privacy filters.
Data storage approval guidelines
The policy should provide guidelines on where and how data can be stored on personal devices to address the safety and storage of critical data. Employees should be taught how to keep company data secure. One way to do this is to use designated folders or secure containers on their personal devices. This approach helps prevent unauthorized access or potential loss.
Employee responsibilities framework
Defining employee responsibilities is central to the policy’s effectiveness. A good BYOD policy clearly explains what employees are responsible for. These include keeping their devices up-to-date and following security rules. It also means immediately reporting any security problems (like suspicious activity or a lost device). This helps employees feel responsible and accountable for keeping information safe.
Reimbursement procedures
A BYOD program needs to have clear rules about how employees will be repaid for work-related expenses on their personal devices. This acknowledges that using their own phones, laptops, etc., can cost them money. The policy should explain the process for getting reimbursed for these work costs. This helps create a fair balance between what the company pays for and what employees pay for.
IT support capabilities overview
A BYOD policy should explain how and when employees can get IT help. This is important for quickly fixing technical problems. The policy needs to include details like what kind of troubleshooting and guidance the IT department will provide. This ensures that personal devices work smoothly with the company’s network.
Exit plan procedures
A BYOD policy must explain what happens when an employee leaves the company. Steps should be outlined for removing company data from their personal device and managing the device itself. This ensures a smooth transition while safeguarding sensitive information.
The policy should also address scenarios where employees lose their devices, are fired, or break a company rule. In these cases, the company must decide if they can remotely delete company information from the employee’s device.
What are the benefits of BYOD?
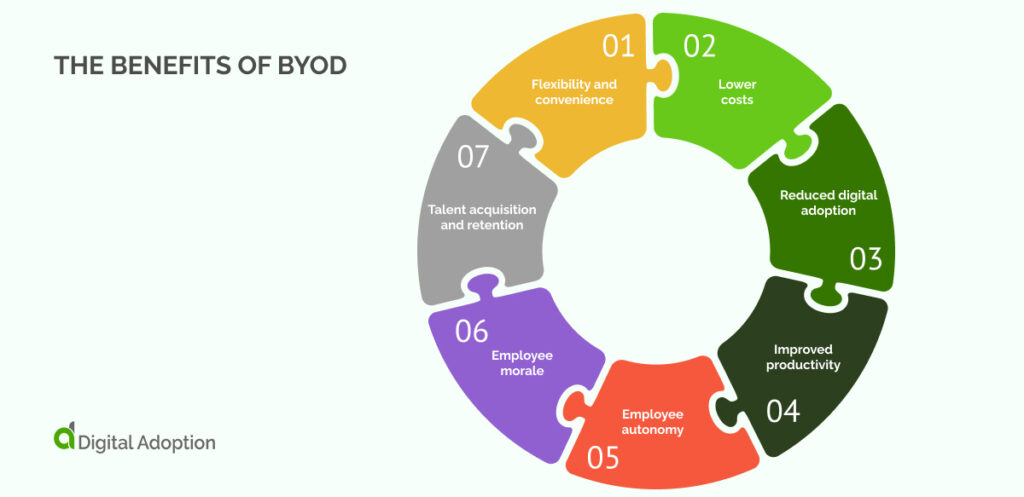
Among the various ways businesses navigate shifting work habits, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies stand out. This solution addresses the needs of modern employees and aligns with the ethos of a connected, tech-savvy workforce.
Let’s delve into the benefits that BYOD brings to the table. These range from enhanced productivity to talent acquisition and retention:
Flexibility and convenience
BYOD epitomizes modern workplace adaptability. Employees can easily switch between work and personal tasks on a single device. This means they don’t need to carry around multiple devices. Employees can access work information whether they’re working from home, traveling, or in a shared workspace. This kind of flexibility creates a culture that emphasizes a healthy work-life balance.
Lower costs
BYOD programs significantly cut business costs. Employees are now responsible for buying and maintaining their own devices. Companies also save money by managing fewer devices, providing less tech support, and buying fewer software licenses.
Reduced digital adoption
BYOD helps employees adjust to new roles quickly. They can use their own familiar devices, minimizing the time to learn new technology. This streamlines the onboarding process and reduces disruptions to their workflow.
Aligning work tools with personal preferences allows for faster tech integration. This ultimately promotes both efficiency and innovation.
Improved productivity
Empowering employees to choose their devices boosts productivity. Employees work more quickly and efficiently when using their own devices, since they already know how to use them. This also means less downtime and better responsiveness when completing work tasks.
Customizable settings enhance the user experience, enabling employees to optimize workflows. This heightened productivity translates into tangible business outcomes and competitive advantages.
Employee autonomy
BYOD grants employees greater autonomy and ownership over work tools. Employees can choose devices that fit their working style instead of using company-issued devices. This ownership generates autonomy, which drives engagement and accountability within the organization.
Employee morale
BYOD initiatives enhance employee morale and satisfaction by accommodating personal preferences. Using familiar devices reduces the hassle of learning new technologies. This also shows employees that their employer’s trust and respects them. Positive reinforcement creates a conducive work environment where employees feel valued.
Talent acquisition and retention
BYOD enhances talent management strategies. These programs can signal that a company has a modern and flexible work environment. This is attractive to tech-savvy employees who prefer to use their own devices. This flexibility can help build a strong employer brand, making recruiting and keeping top talent easier.
What are the challenges of BYOD?
BYOD workplace policies bring various challenges. From security risks to compliance issues and privacy concerns. Let’s explore these challenges in more detail:
Increased security risks
Letting employees use their own devices on the company network increases security risks. This makes it easier for hackers to steal data or access things they shouldn’t. Safeguarding sensitive information becomes a critical priority.
Limited IT support
The diverse array of personal devices presents a challenge for IT support. Providing tech support for all the devices and operating systems employees use can be challenging. This can negatively affect user experience and slow down the company’s operations.
Device diversity dilemma
Managing many devices with distinct operating systems and security settings complicates device oversight. Ensuring all these devices work well together is an ongoing challenge for companies.
Employee pushback
Some employees may not want to use their personal devices for work. They might be concerned about privacy or worry that the company will have too much control over their devices. Successfully navigating this resistance is key to properly implementing BYOD policies.
Data ownership and retrieval
BYOD policies need to define who owns what data. They also need a clear way to get company information back from employees when they leave the company. This can be tricky. Balancing organizational data control and individual privacy is critical.
Limited IT oversight
The decentralized nature of BYOD limits IT oversight. Companies need to monitor personal devices for security but must do so in a way that respects employee privacy. This can be a hard balance to achieve.
Navigating compliance and legal standards
Failure to adhere to legal and compliance standards can quickly turn a good thing bad. This is especially important for those in highly regulated industries (like healthcare or finance). That’s why BYOD policies need to fit with all the legal requirements. This helps reduce the chances of getting in trouble and keeps the company compliant overall.
Lost productivity
Employees might get distracted by personal apps and device features while working. Plus, not all phones, tablets, and laptops are equally powerful. This makes it harder for companies to ensure that all employees can be equally productive when using their own devices.
Data and privacy concerns
Companies need to find a balance between having enough control over devices to keep data safe and respecting employee privacy. Clear policies and open communication can help ease employee concerns about privacy violations.
BYOD vs. other corporate device policies
Besides BYOD initiatives, various other corporate policies play a big role in how modern companies manage devices.
These policies go beyond a one-size-fits-all approach. They reflect the different strategies organizations use to meet the specific needs of their workers.
These models can be combined with existing policies like BYOD to ensure personal devices are used responsibly. A mix of these methods helps to create a flexible and adaptable foundation to support today’s agile firms.
These policies include:
- CYOD (Choose Your Own Device): Employees can select a device from a pre-approved list. This offers a balance between employee preference and reliable device management for the company.
- COBO (Corporate-Owned, Business-Only): Organizations provide devices that are used exclusively for work-related purposes. This gives the company the most control over device configurations and security.
- COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled): The company owns the devices but allows some personal use. This gives employees some flexibility while still letting the company maintain control.
How to ensure safe and secure BYOD practices
Getting a BYOD program up and running can be tough. Tech integrations are complicated, especially for businesses with large-scale operations. The diversity of devices and security considerations in BYOD environments only adds to the complexity.
One solution is to use BYOD Mobile Device Management (MDM) software. This software gives businesses a central place to manage and control the different aspects of personal devices used at work.
MDM software makes deploying, managing, and monitoring approved devices easier. It includes features to protect company data and enforce security. The software can control apps on employee devices and track their usage. If a device is lost or stolen, it can remotely wipe the data. It also automatically installs security updates and helps companies create compliance reports.
Biometric authentication, like fingerprint or facial recognition, makes BYOD programs more secure. Companies can also use two-factor authentication. This requires employees to verify their identity in two different ways. Managing applications is streamlined through app allowlisting/blocklisting, dictating the permissible apps.
A VPN can also enhance connection security, ensuring data transmissions are secure. Device encryption provides a safe enclosure for stored data. Whereas jailbreak/root detection features offer a preventive measure against unauthorized device alterations.
A chain, however, is only as strong as its weakest link. A joint commitment to agile security practices is needed. This is because human error and negligence are prime targets for cyber threats. Purplesec’s research reveals that 97% of companies have faced cyberattacks involving mobile threats and report a 27.4% increase in security breaches within enterprise organizations.
A culture of cybersecurity awareness and accountability should also be made a priority. Active participation from CIOs, CISOs, CDOs, HR personnel, and the company’s employees is needed. When done right, secure BYOD programs create a safe environment for innovation and productivity. Environments where employees can confidently use their devices at work, knowing company data is protected.




![18 Examples of AI in Finance [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/18-Examples-of-AI-in-Finance-2025-300x146.jpg)
![14 Examples of AI in Manufacturing [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/14-Examples-of-AI-in-Manufacturing-2025-300x146.jpg)
![29 Examples of AI in Education [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/29-Examples-of-AI-in-Education-2025-300x146.jpg)
![15 Examples of AI in Retail [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/15-Examples-of-AI-in-Retail-2025-300x146.jpg)
![13 Examples of AI in Healthcare [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/AI-in-healthcare-examples-300x146.jpg)


![18 Examples of AI in Finance [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/18-Examples-of-AI-in-Finance-2025.jpg)
![14 Examples of AI in Manufacturing [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/14-Examples-of-AI-in-Manufacturing-2025.jpg)
![29 Examples of AI in Education [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/29-Examples-of-AI-in-Education-2025.jpg)