The high-octane nature of digital transformation (DX) often requires organizations to adopt an equally zealous stance toward digital investments if they hope to remain agile and outpace competitors.
The social and economic fallout caused by COVID-19 fast-tracked an increased demand for radical digital solutions on an unprecedented scale. The more recent geopolitical tensions between Russia and Ukraine have further highlighted the urgency for digital transformation as global events rapidly reshape industries and markets.
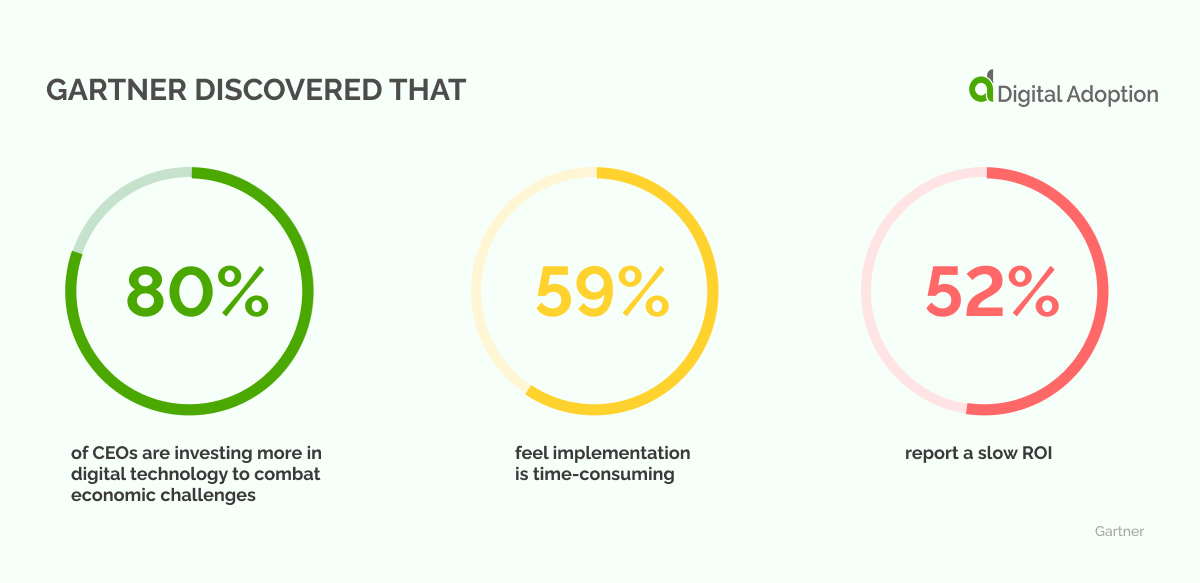
Gartner discovered that 80% of CEOs are investing more in digital technology to combat economic challenges, but 59% feel implementation is time-consuming, and 52% report a slow ROI.
This article explores how digital leaders and CIOs are accelerating their digital transformation efforts. We cover the importance of digital transformation, the benefits of acceleration, and six proven tactics, such as leveraging cloud tech and agile methodologies, to transform operations, enhance customer experience, and generate revenue streams.
The Importance of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is the integration and adaptation of digital technology in all aspects of a business or organization.
Digital transformation is not just for large corporations or tech companies but businesses of all sizes and industries. It is a vital step towards staying relevant and future-ready.
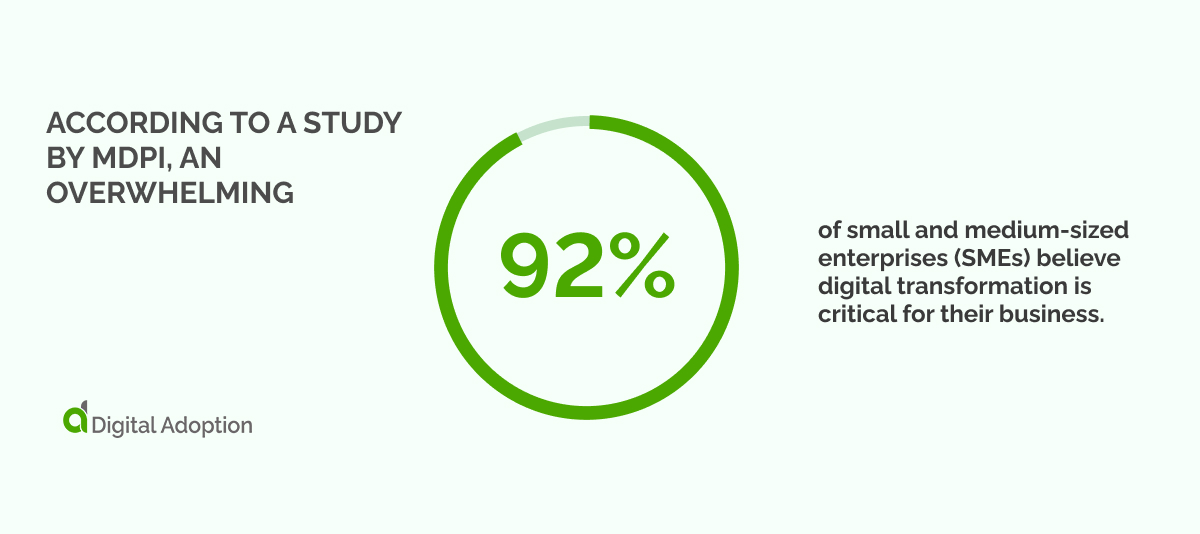
According to a study by MDPI, an overwhelming 92% of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) believe digital transformation is critical for their business.
Ignoring digital transformation could have significant consequences for businesses, including decreased market share, inability to compete, and even failure in the long term.
Digital transformation is more than just integrating technology into business operations. It’s about revolutionizing the way organizations operate in a world that is constantly evolving.
The significance of this transformation cannot be overstated. Businesses need to outmaneuver competitors, maintain and improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and possess the agility and adaptability to succeed.
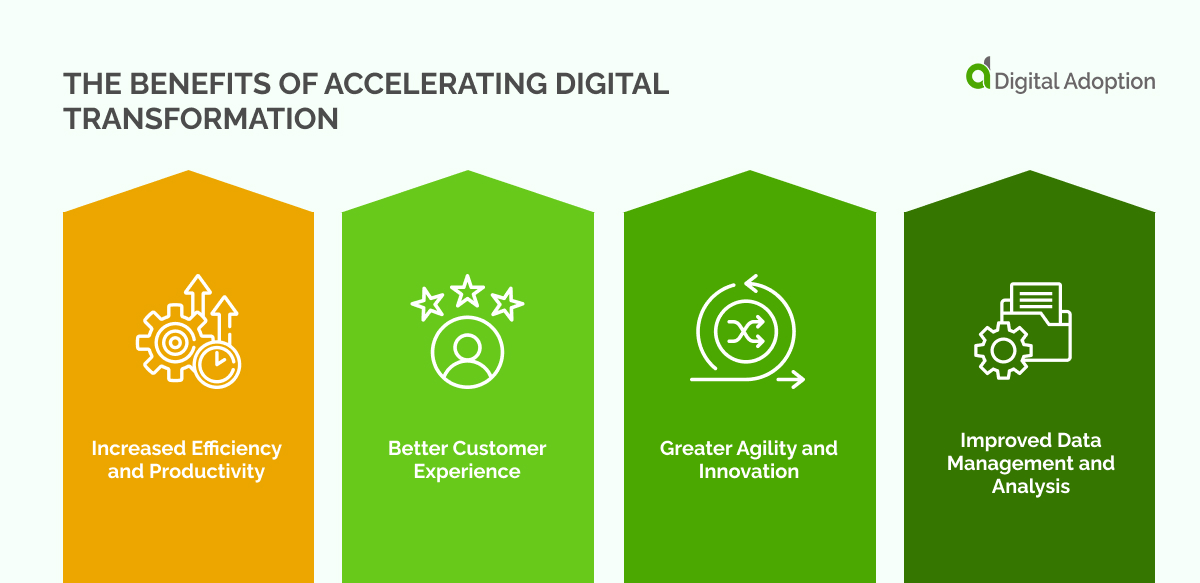
The Benefits of Accelerating Digital Transformation
While digital transformation was once considered a choice for businesses, it has now become necessary.
According to a World Economic Forum report, digital transformation’s potential value across various industries could surpass $100 trillion in the next decade, contributing significantly to the global economy.
As such, by accelerating digital transformation, businesses can reap various benefits. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity
By implementing digital tools such as automation, businesses can minimize manual tasks that waste time and resources. This increases productivity as employees can spend more time on strategic and high-value tasks. Digital transformation can also streamline workflows, reduce errors, and enable real-time collaboration, enhancing efficiency.
- Better Customer Experience
Digital transformation can improve customer experience by providing personalized and seamless interactions throughout their customer journey. This includes implementing chatbots, self-service portals, and social media monitoring to give customers quick and effortless ways to interact with the business. A positive and effortless customer experience increases customer satisfaction, loyalty, and the creation of potential endorsements.
- Greater Agility and Innovation
Digital transformation can enable businesses to rapidly adapt to changing market dynamics, customer preferences, or external factors such as natural events or catastrophes. Cloud-based tools and platforms provide greater flexibility for innovation and enable better team collaboration. This means businesses can quickly develop new products or services and pivot to new opportunities, improving their marketplace viability.
- Improved Data Management and Analysis
Digital transformation can automate the data collection, management, and analysis processes. With large volumes of data being gathered from different sources, digital tools are required to process and analyze data quickly and efficiently. Data-driven insights can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, decision-making, and identifying pain points. Businesses can then use this data to make informed decisions and optimize operations.
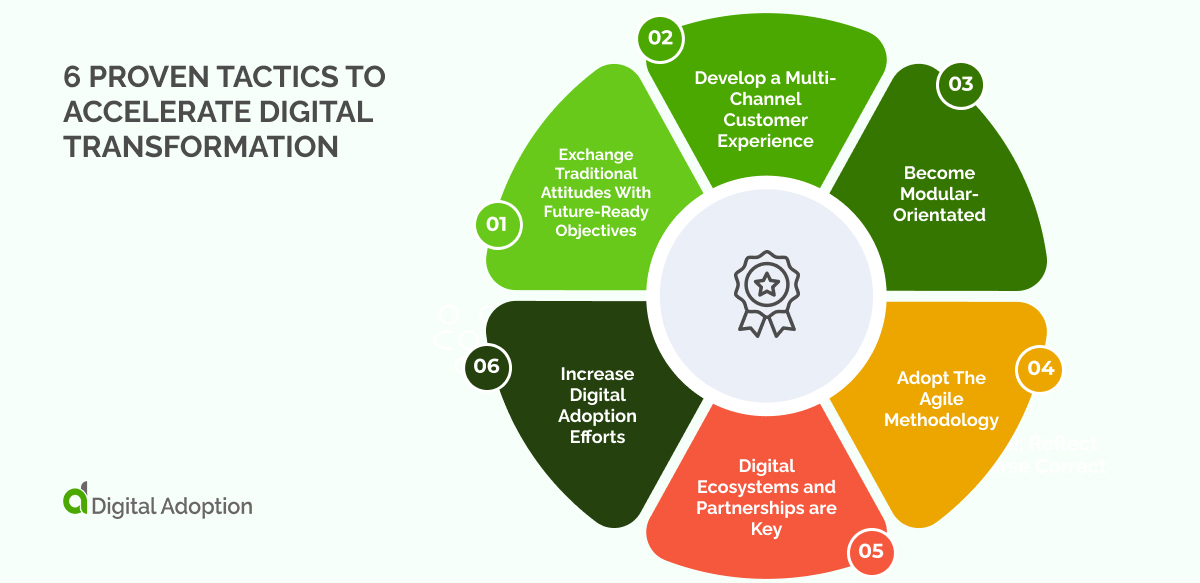
6 Proven Tactics To Accelerate Digital Transformation
-
Exchange Traditional Attitudes With Future-Ready Objectives
Digital transformation requires a significant shift in mindset to adapt to a rapidly changing business landscape. Companies that cling to traditional attitudes risk falling behind their competitors who are willing to embrace innovation, adapt to new technologies, and anticipate customers’ ever-evolving needs.
According to McKinsey’s research, digital transformation initiatives face challenges despite many years of effort, with only a 30% success rate.
Companies need to exchange traditional attitudes with future-ready objectives to accelerate digital transformation. This means fostering a culture of innovation, embracing experimentation, and learning from failures. It also means identifying and adopting new technologies and approaches to streamline operations, bolster CX, and increase speed and agility.
By reframing an organization’s objectives to be future-focused, companies can move beyond incremental improvements and realize new opportunities for growth and success.
This will require ongoing education, collaboration, and communication across all levels of the organization. By taking these necessary steps, companies can overcome resistance to change, leverage new possibilities, and position themselves to better serve their customers in the digital age.
-
Develop a Multi-Channel Customer Experience
To effectively accelerate digital transformation, businesses must prioritize enhancing the customer experience (CX). One effective tactic to accomplish this is launching new products and services that streamline the customer journey across multiple channels, including social media, email, chatbots, and more.
A multi-channel CX approach provides customers with different ways to connect with a brand, ultimately personalizing the CX and improving customer satisfaction.
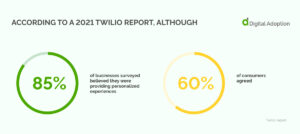
According to a 2021 Twilio report, although 85% of businesses surveyed believed they were providing personalized experiences, only 60% of consumers agreed.
Additionally, employing a multi-channel CX model allows businesses to gather valuable data on customer behavior, allowing for further optimization of digital strategies.
To successfully launch a multi-channel/product CX, it’s critical to understand the target audience and identify their preferred channels. Utilizing analytics and customer feedback can help determine the most effective channels for driving results. Businesses must also ensure they have the technology and resources to manage and track activity across all channels.
-
Become Modular-Orientated
One effective tactic for accelerating digital transformations is to embrace modularity. This means breaking down traditional monolithic systems and creating a set of smaller, independent modules that can be easily combined and scaled as needed.
By taking a modular-oriented approach, companies can rapidly create new digital services that meet the ever-changing needs of their customers.
When each module is developed with a specific purpose, it becomes easier to iterate and improve upon each individually without risking the entire system’s stability.
This approach of becoming modular-oriented to create new digital services can apply to a wide range of companies across industries that are looking to accelerate their digital transformation.
It also emphasizes that each module presents specific purposes that make it easy to iterate and improve on each one independently without affecting the entire system. A modular-oriented approach adds agility to the development process, allowing teams to quickly add, remove, or replace modules without affecting the whole system.
-
Adopt The Agile Methodology
Adopting the agile method is another essential tactic leveraged for accelerating digital transformation within organizations. The methodology emphasizes short, iterative cycles, breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable ones, and continuous testing and improvement of processes.
Agile allows companies to create a responsive and adaptable digital environment that can handle the quick changes and disruptions in today’s business world. It promotes collaboration and transparency, enabling teams to work more proficiently and reducing delays or miscommunication.
Statistics from KnowledgeHut reveal that implementing the Agile methodology has led to significant benefits for organizations. Specifically, 63% have reported an enhancement in their ability to manage changing priorities, 47% have experienced improved business/IT alignment, and 42% have seen an enhancement in software quality.
To get started with agile, organizations should establish cross-functional teams empowered to collaborate independently, focusing on delivering value to customers. These teams should be free to experiment, iterate, and adapt as needed, using data-driven insights to inform their decisions and actions.
Embracing the agile method provides a nimble, responsive, and collaborative work environment better suited to meet the demands of digital transformation.
-
Digital Ecosystems and Partnerships are Key
Digital transformation is not a solo endeavor. Building a digital ecosystem and forming strong partnerships is key for companies to accelerate their transformation.
What is a digital ecosystem? Simply put, it’s a network of individuals, businesses, and organizations collaborating to create and deliver value through digital interactions. By cultivating a digital ecosystem, companies can reach more customers, access more resources and share knowledge with other organizations.
Partnerships are also essential for success in digital transformation. Companies can benefit from partnering with other trusted industry experts to build out their digital capabilities, learn new skills, and gain access to new markets. By pooling resources and knowledge, partnerships can drive innovation and create new growth opportunities.
It’s important to choose partnerships and build ecosystems wisely. Digital ecosystems and partnerships should align with your company’s goals, values, and overall strategy.
Companies should also consider the necessary infrastructure and technology needed to support their partnerships and ecosystem.
-
Increase Digital Adoption Efforts
It is crucial to have a clear plan for adopting new digital tools and applications during digital transformation.
Many companies invest significant resources in implementing new technologies but fail to consider how their employees and stakeholders will adopt them.
To increase digital adoption, it’s essential to communicate new tools’ benefits and provide users with adequate training and resources. This can be facilitated through specialized software solutions such as Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs) that offer a range of interactive and personalized training tools to help users learn new applications at their own pace.
Digital adoption platforms (DAPs) are tailor-made software solutions equipped with several advanced tools and resources to facilitate the adoption of digital applications. Companies can efficiently steer through their digital transformation journey without requiring to master coding skills by utilizing these platforms.
Our research has unveiled the revenue generated by select companies offering digital adoption platforms (DAPs) in 2022, and the findings are significant.
Walkme has emerged as the clear leader, generating $178 million in earnings. Pendo secures the second position among the top earners with $100 million in revenue, while Whatfix follows closely in third place with $17.4 million in revenue.
In addition, a strong change management strategy is also required to ensure that all relevant stakeholders are on-board with the adoption process and that any potential roadblocks are addressed proactively. By increasing digital adoption efforts, companies can effectively leverage new technologies to accelerate their digital transformation journey.
Why Accelerate Digital Transformation?
Future-ready businesses must embrace digital transformation to unlock new opportunities and potential growth. The global COVID-19 pandemic has only emphasized accelerating this process and innovating much quicker.
By accelerating digital transformation, businesses can improve operational efficiency, minimize costs, and offer customers a well-rounded experience. As such, embracing new technologies, e.g., automation, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, will further enable businesses to streamline their processes and increase business velocity.
According to Zippia, global spending on digital transformation is expected to reach $6.8 trillion by 2023. Unsurprisingly, digitally mature companies are reportedly 23% more profitable than their less mature counterparts.
The disruption caused by digital transformation has given businesses the tools required to better understand their customers’ needs and behaviors. By leveraging these six proven tactics, companies can increase customer loyalty, enhance retention, and drive growth.