Emergent AI abilities refer to the unexpected, novel behaviors or skills that appear in advanced artificial intelligence systems. These abilities are not pre-trained or programmed into the AI model but emerge unpredictably, particularly in large-scale models.
Despite the term’s exciting implications, many researchers argue that these ’emergent abilities’ are often a result of increased computational capability rather than a sudden leap in AI cognition.”
We’re far from the “rise of the machines” that the Terminator films predicted in the 1980s, with armies of robots aggressively taking over the world!
But as the capabilities of generative AI models move on, some researchers are seeing “sparks” of a deeper intelligence in AI. In other words, we see how AI models can sometimes complete tasks they were not programmed to do.
Researchers use the word emergence to describe these surprising skills.
When you hear phrases like emergent abilities, emergent properties, or emergent capabilities, we’re talking about the unprogrammed skills of AI. While this is still a very new field, new research is shining a light on AI’s emergent abilities, and AI users are starting to wonder about the potential for this new technology.
This article will look into the new field of emergent AI. It will:
- Explain the meaning of emergent AI abilities;
- Introduce several examples of emergent AI in practice;
- Suggest some future directions for emergent AI.
Emergent AI abilities are important to understand. According to McKinsey, as much as 79% of workers have now been exposed to uses of generative AI. As time goes forward, the majority may need to detect and utilize emergent abilities.
So, we must do our best to prepare.
What are emergent AI abilities?
An AI Tool has “emergent AI abilities” when it can complete tasks it was not specifically programmed to do. The AI system works, and something new happens, like magic.
Emergent AI abilities may come as a surprise to the developers. Or, researchers might make experimental situations in which AI can seek a way to answer a problem – even though they weren’t told explicitly how to make the answers.
Emergent AI is an exciting thing. But right now, we don’t know how harmful they might be. So, Emergent AI is a part of AI risk management.
AI’s emergent capabilities are in the news because of fresh research. In an extensive research paper from April, Microsoft researchers found the “sparks” of emergent behavior in ChatGPT. But in the same month, Stanford researchers found that this behavior may be a “mirage.”
By the way, the word “emergent” here has a special meaning. Emergent behavior happens when a complex entity does things that its parts do not. Termite mounds, snowflake formation, and human language can all give examples of emergence. Emergent AI abilities are the same: the parts do something new.
So, you must be careful when you hear “emergent AI.” Some folks will use it to talk about new and innovative uses of AI.
For example, “emergent AI” is a key theme for the Gartner 2023 emerging technology hype cycle. To be clear, this article will not discuss emerging AI technologies. We will only talk about the emergence of artificial intelligence.
Examples of emergent AI abilities
Here’s a warning, though.
A casual observer won’t be astonished by the current emergent capabilities of large language models.
Right now, the emergent capabilities of AI won’t suddenly make your profits skyrocket.
All the same, emergent abilities in large AI models are fascinating. Let’s take a look at some classic examples.
- In the 1980s, computer scientist Craig Reynolds introduced the Boids program, a simulation illustrating how bird-like entities can mimic real birds’ flocking and formation movements. This model serves as a compelling example of how intricate collective behavior can emerge from the interplay of straightforward local rules.
- Microsoft’s research brings forth a range of straightforward examples to help assess emergent behavior. These simple tasks indicate “sparks” of genuine emergence – and perhaps artificial general intelligence. For instance, Microsoft’s research demonstrates that GPT-4 can proficiently infer characters’ mental states and identify cases of miscommunication and misunderstanding, akin to passing the Sally-Anne false belief test. Small milestones like this show the limits and possibilities of generative AI.
- The tech giant Google’s DeepMind subsidiary has unveiled remarkable AI cases. DeepMind’s AlphaZero, a chess-playing AI showcased in a 2018 article in Science, showcases extraordinary prowess in mastering the game. Furthermore, DeepMind created a team of digital humanoids that learned to play football autonomously. While they comprehend the objective and possess essential tools, they were not specifically programmed to handle the inherent unpredictability of this sport. This underscores the captivating unpredictability of AI’s emergent capabilities.
Some reports of emergent abilities in AI may, however, be exaggerated. For example, CEO Sundar Pichai suggested that Google’s Bard had learned Bengali independently, but fact-checkers later pointed out that the model was initially trained in Bengali.
Risks of Emergent AI
Leaders in AI research are alert to the risks of emergent AI capabilities. As Demis Hassabi, the head of DeepMind, reminded us in October 2023, “The next few generations maybe when they have extra capabilities like planning and memory and other things … They will be phenomenal for good use cases, but also they will have risks.”

Therefore, artificial intelligence leaders should try to understand the unpredictable abilities that AI could be capable of in the future.
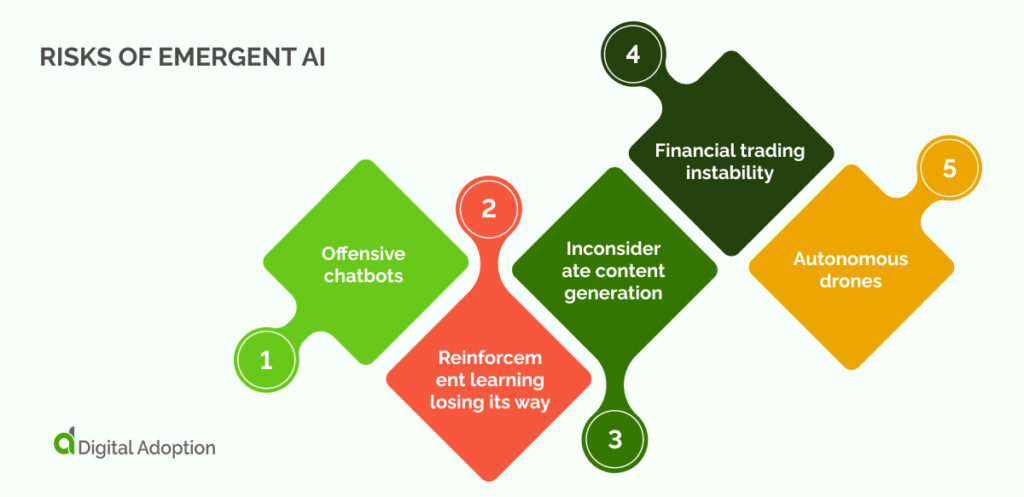
Let’s take a quick look at some of the major risk areas:
- Offensive chatbots. Chatbots with machine learning capabilities may sometimes generate inappropriate, profane, or biased responses due to unpredictable emergent behavior based on user interactions.
- Reinforcement learning is losing its way. In reinforcement learning, AI agents learn by trial and error. Unpredictable emergent behavior might result in unintended actions, such as a robot learning to exploit a system or finding novel ways to complete an unsafe or ethical task.
- Inconsiderate content generation. AI systems for content generation can sometimes produce content that violates copyright, infringes on privacy, or spreads misinformation, leading to unpredictable consequences.
- Financial trading instability. High-frequency trading bots can exhibit unpredictable behaviors, leading to market volatility and economic instability if they trigger rapid, unexpected fluctuations.
- Autonomous drones. Autonomous drones with unpredictable behavior may pose risks in areas like surveillance, privacy invasion, or accidental collisions.
Researchers and developers are building more robust, interpretable, and controllable AI systems to address the potential negative consequences of unpredictable AI emergent abilities, and policymakers are considering regulatory frameworks to ensure responsible AI deployment.
These consequences are just risks; we don’t know if they’ll come true. And, in the future, we may realize that we were worried about nothing. Stanford University researchers suggested that Emergent abilities were just a “mirage”: created because of how we measure them, not because of their actual abilities.
Should you plan for emergent capabilities today?
For business-level end users, the intricacies of emergent AI abilities need not be a primary concern today.
Instead, the focus should be on remaining vigilant about the broader risks related to emergence and bias. This is an ideal moment to ensure the proper functioning of your “shadow AI,” implement clear AI policies, and verify the overall health of your software. If issues arise, address them promptly.
Conversely, AI researchers should prioritize acquiring a comprehensive understanding of emergence. They should be adept at recognizing emergent capabilities as they surface and conducting thorough exploration and analysis.
While many aspects of AI emergence remain shrouded in mystery, it’s foreseeable that this domain may soon become the forefront of digital risk management.
Stay prepared, as the future promises further intriguing developments in AI’s emergent abilities.













