AI risk management is the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating the potential risks associated with the use and deployment of artificial intelligence technologies.
Worries about the ethical application of AI continue to persist. posing risks to individuals and employees, and more extensively, a breach of universal human rights If not correctly used.
Developed collaboratively by private and public sectors, frameworks such as NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework provide guidance on managing AI risks to individuals, organizations, and society at large.
It’s a flexible approach designed to guide AI development both domestically and internationally, aiming to reduce issues like discrimination, security threats, and environmental impacts.
Organizations such as the Department of Energy also offer comprehensive guides like the AI Risk Management Playbook for identifying and recommending mitigations for AI-related risks.
As AI becomes intertwined with daily life and business operations, implementing robust and effective AI risk management strategies is becoming essential to ensure the responsible and safe utilization of this powerful technology.
In 2022, Statista reports that businesses using AI are mainly focusing on managing cybersecurity risks, with over half actively taking steps to address these threats.
This article will:
- Explore the various types of AI-related risks
- Provide an overview of the current risk management frameworks available to help organizations mitigate these risks.
By the end of the article, you will have a better understanding of how to effectively manage AI-related risks and ensure their responsible use.
What Is AI Risk Management?

AI risk management is a crucial process that helps identify, evaluate, and address potential issues associated with the use of artificial intelligence (AI). Imagine you’re using a satnav to get from A to B.
Now, if the satnav steers you down the wrong path, you’d want to have a system in place to correct this error and avoid similar mistakes in the future. That’s essentially what AI risk management does.
In a nutshell, it’s like a safety net for AI, ensuring that the technology is used responsibly and ethically. It takes into account various factors, from rogue IT and privacy concerns to potential security threats, and aims to prevent any harm these might cause to individuals, organizations, or society as a whole.
A number of frameworks exist to guide this process, such as NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework and the Department of Energy’s AI Risk Management Playbook. These provide detailed guidelines on how to handle potential risks, ensuring that AI technology can be both beneficial and safe.
So, while AI continues to evolve and become more integrated into our daily lives, AI risk management remains a vital tool in ensuring we harness its power responsibly.
Why Is AI Risk Management Important?
As our embrace of digital technology deepens, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a prominent feature in our everyday lives. AI digital adoption is growing across industries and countries, with the technology being used for everything from healthcare to banking.
However, with this rapid adoption of AI has come a heightened awareness of its potential risks. It’s important that organizations take active steps to assess and mitigate any risks associated with their AI technologies in order to ensure responsible use.
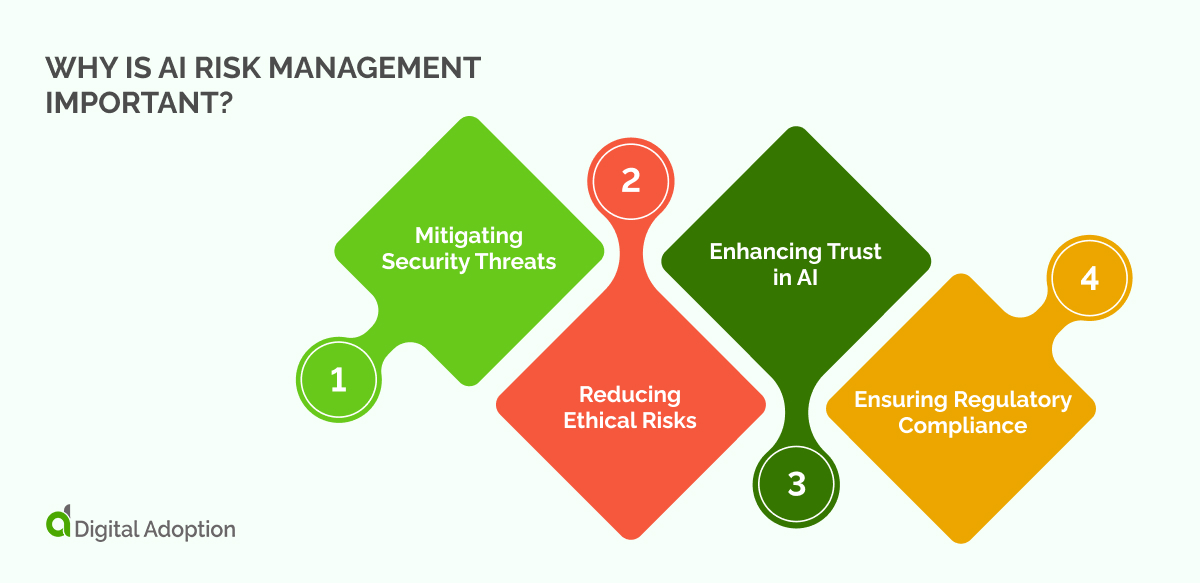
Here’s why it’s so crucial:
Mitigating Security Threats
- AI systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches, especially as digital adoption increases. These threats can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and privacy violations.
- AI risk management helps identify these potential vulnerabilities and puts measures in place to counteract them, ensuring that our digital world remains secure.
Reducing Ethical Risks
- AI has the potential to inadvertently discriminate or cause harm due to biases in its programming or data. This is particularly risky in areas like hiring or lending, where AI decisions can have real-world impacts.
- AI risk management helps ensure that AI operates ethically and fairly, protecting individuals from potential harm.
Enhancing Trust in AI
- As digital adoption grows, so does our reliance on AI. However, if people don’t trust AI, they won’t use it.
- AI risk management helps build this trust by showing that AI systems are reliable and safe, encouraging further digital adoption.
The application of AI, despite posing certain risks, may also serve as the solutions for mitigating these risks.
Gartner predicts that over the next three years, more than 40% of privacy compliance technology will depend on AI.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
- As AI becomes more prevalent, regulations are evolving to keep pace. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal issues.
- AI risk management ensures that AI systems comply with these regulations, helping organizations avoid legal pitfalls.
AI Risk Management Framework
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a powerful tool that can revolutionize industries and lives.
However, it’s not without risks. To mitigate these risks, an AI risk management framework is essential. This framework aims to identify, assess, and manage potential threats associated with the use and deployment of AI.
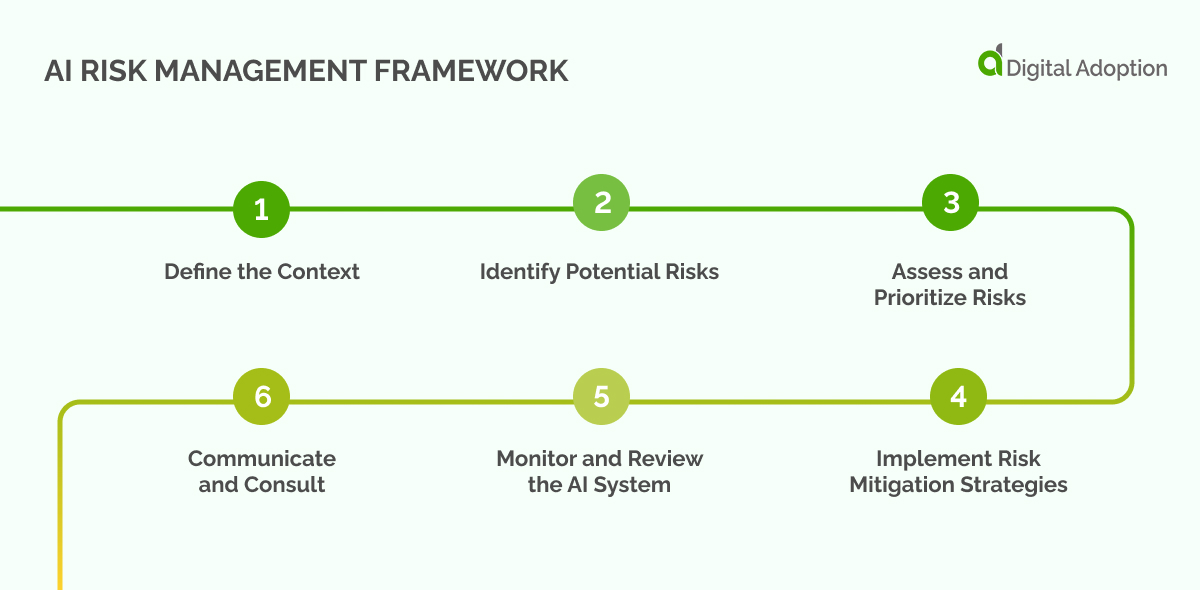
Here’s a suggested structure for such a framework:
1. Define the Context
Firstly, understand the context in which the AI system will be used.
Consider the following:
- Purpose of AI: What tasks will the AI system perform? How will it support your organization’s objectives?
- Environment: What is the legal, social, and economic environment in which the AI system will operate?
- Stakeholders: Who are the people or entities affected by the AI system? These could include employees, customers, or regulators.
2. Identify Potential Risks
Once you have defined the context, the next step is to identify potential risks. This can be done through several methods, such as brainstorming, conducting interviews, or using risk identification tools.
Some common AI risks include:
- Data Privacy Risks: AI systems often rely on large amounts of data, which can lead to privacy concerns if not handled correctly.
- Security Risks: AI systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, leading to potential breaches of sensitive information.
- Ethical Risks: AI systems can inadvertently discriminate or cause harm due to biases in their programming or data.
- Legal and Compliance Risks: As AI becomes more prevalent, regulations are evolving to keep pace. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal issues.
3. Assess and Prioritize Risks
Once potential risks have been identified, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate each one based on its likelihood of occurring and the potential impact it may have.
This comprehensive assessment will aid in prioritizing which risks should be addressed first, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively. Utilizing tools such as risk matrices or decision trees can be highly beneficial in facilitating this process, as they provide a structured framework for analyzing and visualizing the various risk factors involved.
Considering the probability and severity of each risk enables organizations to make informed decisions and develop proactive strategies for mitigating potential negative impacts. A meticulous approach to risk evaluation, coupled with the use of appropriate tools, ultimately contributes to a more robust risk management framework, thereby enhancing overall organizational resilience.
4. Implement Risk Mitigation Strategies
For each identified risk, it is crucial to develop and implement a comprehensive mitigation strategy. These strategies could include a range of measures to address different aspects of risk management:
- Preventive measures: Implementing robust security protocols and data anonymization techniques can significantly reduce the likelihood of data breaches or privacy violations. For example, incorporating encryption algorithms and access controls can safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
- Detective measures: Deploying advanced monitoring systems and real-time alert mechanisms can help identify potential issues early on. This proactive approach enables prompt intervention and minimizes the impact of any security incidents or operational disruptions. Regular vulnerability scans and threat intelligence analysis can further enhance the detection capabilities.
- Corrective measures: Establishing clear procedures and response plans is vital for effectively addressing and rectifying any problems that may arise. This includes developing a well-defined data breach response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. Additionally, creating a robust incident management process and conducting post-incident analysis can help identify areas for improvement and prevent similar incidents in the future.
5. Monitor and Review the AI System
Effectively managing the risks associated with AI is an ongoing and complex endeavor that necessitates continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation.
It is crucial to regularly assess the effectiveness of your risk mitigation strategies by conducting routine audits performance reviews, and actively seeking feedback from stakeholders.
These proactive measures ensure that potential risks are promptly identified and addressed, maintaining a comprehensive approach to managing AI risks. By remaining vigilant and making necessary adjustments, you can enhance the resilience and reliability of your AI systems, fostering trust and confidence among stakeholders.
6. Communicate and Consult
Effective communication and consultation with all stakeholders are crucial throughout the process. This includes consistent engagement with internal stakeholders, such as employees and management, to ensure alignment and clarity.
Additionally, maintaining open lines of communication with external stakeholders, such as customers, regulators, and the public, is vital for transparency and building trust. Regular and transparent communication fosters an understanding of the AI system’s risks and their management, enabling everyone to actively participate in risk mitigation strategies.
Involving all stakeholders in the communication process allows organizations to enhance collaboration and ensure the successful implementation of the AI system.
What Comes After An AI Risk Management Framework?
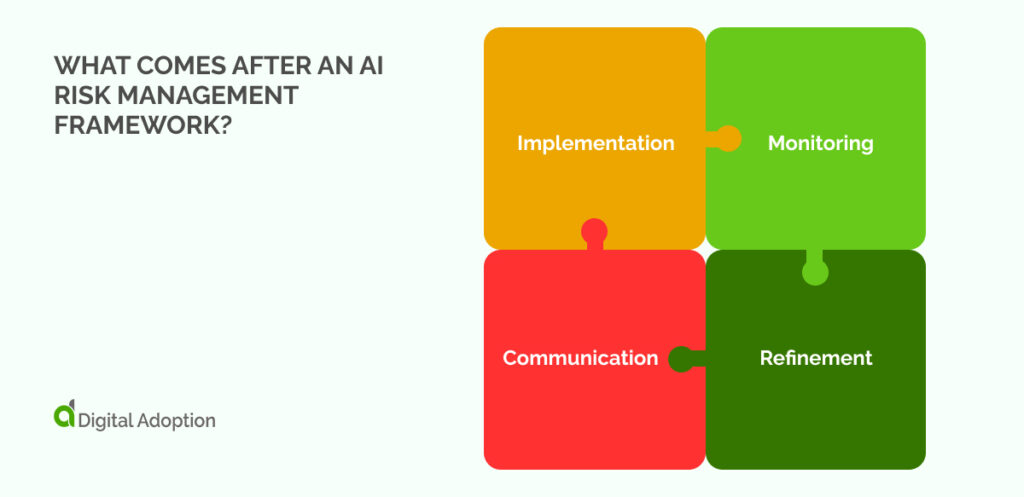
Once an AI Risk Management Framework is in place, the next steps involve its execution and continuous refinement.
These steps can be broken down into several key areas: implementation, monitoring, refinement, and communication.
Implementation: This involves putting the strategies and protocols outlined in the framework into action. It includes setting up necessary systems, training personnel, and integrating AI solutions into existing processes. According to the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, this stage involves a consensus-driven, open, transparent, and collaborative process.
Monitoring: The implemented strategies need to be continually monitored to ensure they are working as intended. This could involve regular audits, performance reviews, or stakeholder feedback. According to the Department of Energy’s AI Risk Management Playbook, this stage also involves AI risk identification and recommended mitigations.
Refinement: Based on the results of the monitoring process, the framework may need to be refined. This could involve tweaking existing strategies or developing new ones to better manage risks. The framework introduced by NIST comprises four functions broken down to develop an AI risk management process.
Communication: The results of the monitoring and refinement processes should be communicated to all stakeholders. This includes internal stakeholders like employees and management, as well as external ones such as customers, regulators, or the public.







![18 Examples of AI in Finance [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/18-Examples-of-AI-in-Finance-2025-300x146.jpg)
![14 Examples of AI in Manufacturing [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/14-Examples-of-AI-in-Manufacturing-2025-300x146.jpg)




