Optical character recognition (OCR) has quietly evolved from a niche backend tool to an enabler of digital workflows.
Once limited to basic text extraction, today’s AI-driven OCR can interpret handwriting, understand document structure, and even detect context across multiple languages and formats. This leap has recast OCR into a calculated asset for industries automating all manner of things, including AI compliance, user onboarding, and data intelligence.
As AI models sharpen their ability to perceive nuance, OCR is now decoding the hidden logic, intent, and relationships embedded within unstructured information.
This article explores OCR, highlighting its evolution from a simple text extraction tool to an AI-powered technology that can interpret handwriting, analyze complex structures, and process a wide variety of text formats.
What is optical character recognition (OCR)?
Optical character recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text into machine-readable data.
It enables systems to extract information from scanned documents, images, or PDFs and turn it into editable, searchable content. For example, a financial services firm can use OCR to process handwritten loan applications, automatically extracting customer details and feeding them into backend systems without manual entry.
AI adoption is dramatically expanding the capabilities of OCR. Modern AI-driven solutions for OCR recognize characters and understand document layouts, infer missing fields, and even validate extracted data against external databases.
This is powering first-class integrations across CRM platforms, ERP systems, and automated compliance workflows. AI business models now allow OCR to adapt to variations in handwriting, non-standard forms, and multilingual inputs with minimal human correction.
OCR now operates as a native intelligence layer within digital ecosystems, bridging unstructured content with automated workflows, analytics, and decision engines.
How does OCR work?
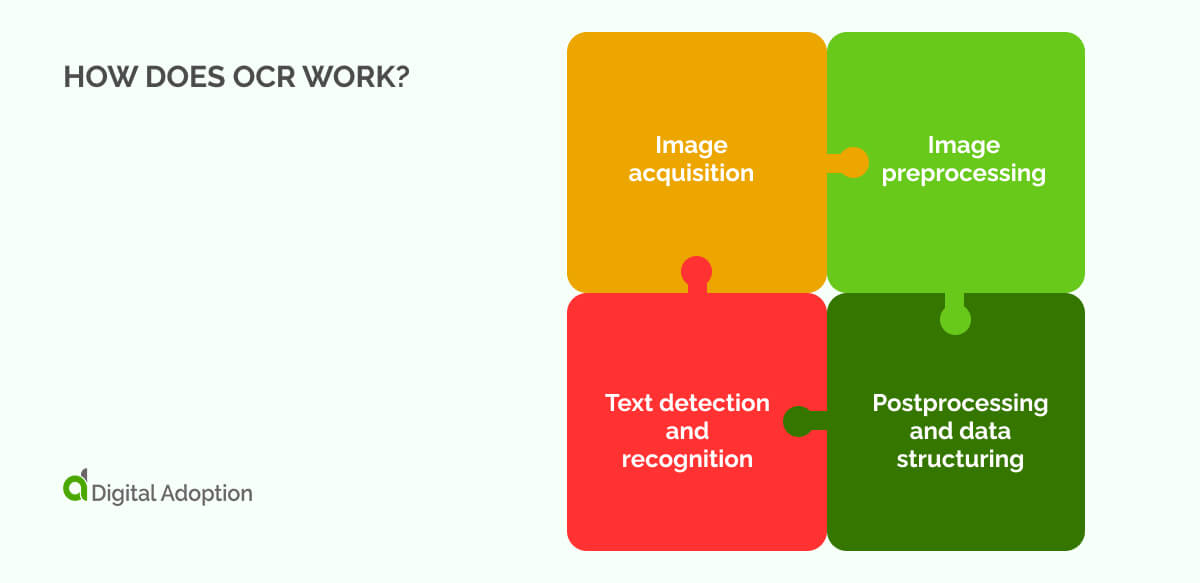
Before OCR can turn documents into usable data, it follows a precise sequence of steps designed to clean, interpret, and convert visual information. Each stage ensures accuracy, consistency, and reliability on a large scale. Let’s discover how OCR works:
Image acquisition
OCR begins with capturing the document using a scanner, camera, or mobile device. The system converts the image into binary data, separating light areas as background and dark areas as potential text zones. Accurate segmentation at this stage is crucial, as it frames how well the system can isolate individual characters and lines later.
Image preprocessing
Before recognition, the image is refined to reduce distortions. Preprocessing techniques include deskewing tilted scans, despeckling noise artifacts, smoothing character edges, and removing background lines or boxes. Systems also detect and classify different scripts if the document contains multiple languages, preparing the content for accurate parsing.
Text detection and recognition
Text recognition relies on two complementary approaches. Pattern matching compares entire character shapes (glyphs) against a database of known patterns, effective for documents with standardized fonts. Feature extraction analyzes structural elements like strokes, curves, intersections, and loops to recognize text even when fonts vary or characters are partially degraded.
Postprocessing and data structuring
Once characters are identified, the system reconstructs the document’s logical structure. It corrects errors based on language models, reconstructs paragraphs and tables, and formats the extracted text. Final outputs can include editable text files, searchable PDFs, or direct data integrations with content management systems and databases.
What are the types of OCR?
OCR technology comes in several forms, each designed to serve different data extraction needs. These types of OCR systems range from basic character recognition to more advanced solutions that can transform data and interpret context-rich documents.
Let’s take a more in-depth look at the different types of OCR:
Simple OCR software
Simple OCR software focuses on basic text recognition. It captures printed characters and converts them into machine-readable data. These systems excel at processing typed documents in clear fonts, such as books or reports. However, they struggle with handwriting or distorted text, making them most useful for standardized documents where clarity is the most important aspect.
Intelligent character recognition software
Intelligent character recognition (ICR) is an advancement over simple OCR, incorporating machine learning algorithms (ML) to recognize handwritten text. ICR can adapt to various handwriting styles, which is particularly useful for documents like forms or surveys filled out by hand. Ongoing training means ICR improves its accuracy, making it more versatile for industries relying on handwritten data, such as healthcare and finance.
Intelligent word recognition
Intelligent word recognition (IWR) takes ICR a step further by focusing on recognizing entire words instead of just individual characters. It understands the context of words within a sentence, improving accuracy, especially for cursive or non-standard fonts. This makes IWR effective in scenarios where both print and cursive handwriting coexist, such as customer feedback forms or mixed-text documents.
Optical mark recognition (OMR)
Optical mark recognition (OMR) is designed to detect marks made on pre-defined forms, such as checkboxes or fill-in-the-bubble responses. Commonly used in surveys, exams, and ballots, OMR systems are highly accurate at reading scanned forms. It’s particularly useful when dealing with large volumes of structured data mining and collection where the response format is standardized.

What are the benefits of OCR?
OCR technology has advanced far beyond basic text recognition and is now integral to automating processes and handling data in the 21st century.
With AI driving these advancements, OCR now supports more complex tasks, allowing businesses to have greater precision and control over their information management.
Let’s take a look at the benefits of OCR:
- Searchable text: OCR transforms static documents into searchable, actionable data, cutting down the time spent manually sorting and retrieving information.
- Operational efficiency: Automating data extraction from forms and documents accelerates workflows, minimizing human error and reducing bottlenecks in processing.
- AI integration: OCR, when paired with AI, adapts to varied handwriting and complex layouts, making it indispensable for industries like healthcare and finance where accuracy is paramount.
- Automating document workflows: OCR eliminates manual routing and categorization, allowing for faster document processing and more efficient information distribution.
- Save on paper record storage: Digital document management reduces physical storage, lowering costs and mitigating the risks of document loss or damage.
- Secure and centralized data: OCR centralizes data, meaning access control and protection against disasters like fires or theft, while maintaining regulatory governance, risk, and compliance (GRC).
What are the challenges of OCR?
OCR technology faces several challenges that can impact its accuracy and effectiveness in real-world applications.
Tackling these challenges is vital to maximizing OCR accuracy and ensuring it delivers reliable results in critical business operations.
Let’s take a look at the challenges of OCR:
- Low-quality images: Blurry or poorly scanned documents create errors in text recognition, especially when resolution is inadequate. Investing in higher-quality scanners or ensuring optimal lighting can mitigate this issue.
- Inconsistent document formats: When documents differ in layout or structure, traditional OCR struggles to adapt, often leading to misinterpretation. Universal file converters can standardize formats before processing.
- Limitations with languages and character sets: OCR systems struggle with foreign languages and special characters. To improve accuracy, select OCR solutions with robust multilingual and alphanumeric support.
- Text skew and distortion: Skewed or warped documents confuse OCR engines. Pre-processing techniques like image alignment and skew correction can address this challenge.
- Challenges with non-text elements: OCR struggles to recognize embedded graphics, tables, and logos accurately. Specialized systems or pre-processing steps to filter non-text elements help maintain text correctness.
- Privacy and security risks: Handling sensitive data through OCR requires strict security measures to prevent breaches and ensure data ethics are upheld.
What are some common OCR use cases?
Understanding OCR use cases is the next step in exploring its potential. This step helps businesses pinpoint where OCR can deliver the most impact, whether in digitizing contracts, processing forms, or analyzing invoices.
Let’s look at some of the most prominent use cases for OCR:
Generative AI for text extraction
AI-driven text extraction can rapidly process data from scanned documents, eliminating much of the manual entry. Automating this task helps businesses heighten both speed and accuracy, reducing human error.
Image preprocessing for OCR
Before OCR recognition, image preprocessing improves document clarity, especially for older, blurry records. This step helps organizations like nonprofits digitize and preserve crucial historical data with greater accuracy.
Text segmentation in OCR
In auditing processes, OCR helps separate relevant transaction data from crowded spreadsheets. This feature ensures that key information is easily identifiable and can be analyzed with precision.
Character recognition processing
OCR’s character recognition technology converts handwritten documents into digital formats, preserving them for the future. This capability is crucial for historical archives, as it allows handwritten texts to be searchable and accessible.
Language modeling and text correction
Applying language models means OCR systems can fix misread text during scanning. This capability maintains the quality and accuracy of the original content while digitizing manuscripts or documents.
Layout analysis for OCR
Real estate professionals can scan blueprints with OCR to maintain alignment and format. The result is a digital version that mirrors the original, making it easier to share and edit.
Handwriting recognition (ICR)
ICR is perfect for converting handwritten essays into editable text. Teachers can digitize students’ work, improving their ability to grade and organize assignments quickly.
Export-ready document assembly
Once OCR extracts invoice data, it can automatically be formatted into a clean PDF. This automated workflow saves time for logistics companies and improves the efficiency of document processing.
Searchable tagging and metadata generation
OCR software makes it easy to tag and categorize scanned field notes. Research teams can then locate key data points, reducing the time spent searching through vast collections of information.
Automated data extraction
HR departments use OCR to extract contact information from resumes, automating the tedious data-entry process. This technology helps streamline candidate evaluation and speeds up the hiring process.
Image-based text search
With OCR, eCommerce businesses can turn product images into searchable text. This improves catalog navigation, making it easier for customers to find what they need in the age of digital convenience.
What does the future hold for OCR?
OCR has come a long way from its origins, adapting to more sophisticated requirements and becoming a tool for businesses to convert and structure data from documents with complex layouts and formats.
According to ResearchGate, advancements in OCR are increasingly shaped by deep learning techniques that focus on enhancing text recognition across different layouts and fonts. As these systems evolve, OCR continues to become more adaptable and efficient, better handling complex documents with varying characteristics.
The integration of computer vision and natural language processing (NLP) is pushing OCR capabilities further, allowing deeper document understanding, even from low-quality or irregular sources.
As generative AI reconfigures and enhances OCR’s efficiency, businesses can expect faster and more precise data extraction, which goes a long way in shaping overall operations.
The future promises further refinements, making OCR an indispensable part of any digital strategy.
People Also Ask
-
How accurate is OCR?OCR accuracy depends on factors such as image quality, text clarity, and the systems sophistication. Advanced OCR systems can achieve high accuracy rates, especially with well-structured and high-resolution documents. However, challenges arise with noisy, distorted, or poorly lit images, impacting performance. Enhanced algorithms reduce errors over time.
-
Can OCR read images with tables or forms?OCR can read images with tables or forms, but the complexity of the layouts may affect accuracy. Systems equipped with advanced layout detection and structure analysis handle forms and tables more effectively, preserving their original format. However, intricate or highly formatted tables can still present challenges for OCR tools.
-
Does OCR support handwriting?OCR can support handwriting recognition through Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR). While it performs well on legible handwriting, accuracy drops with messy or inconsistent handwriting styles. Modern OCR systems continuously improve in handwriting recognition, but some level of error may still occur, especially with non-standard scripts.

 FACT CHECKED
FACT CHECKED







